Fig. 2.
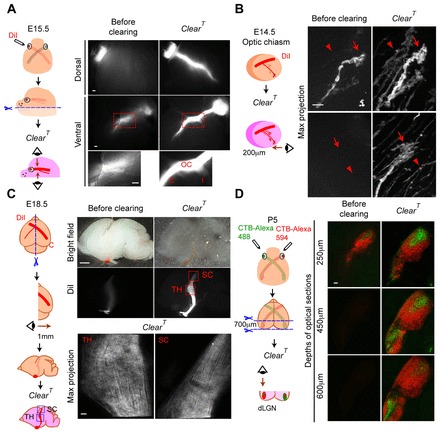
Retinal axon projections in brain tissue cleared with ClearT. (A) E15.5 eye was labeled with DiI, the jaw and tongue were cut away and the head was cleared with ClearT. DiI-labeled contralateral (C) and ipsilateral (I) retinal axons and optic chiasm are detected in both dorsal and ventral views after clearing with ClearT. (B) Merged stack (41 images, 5 μm steps) of E14.5 DiI-labeled growth cones (GCs) (arrows) and axons (arrowheads) of the ipsilateral optic tract; imaged from the ventral surface of 200 μm brain section, before and after clearing. (C) DiI-labeled contralateral RGC projection to the thalamus and superior colliculus at E18.5. Brains were cut sagittally at the midline and cleared with ClearT. Merged stack (51 images, 20 μm steps), viewed from the midline. DiI-labeled RGC axons in the dLGN in the thalamus (TH) and superior colliculus (SC) were undetectable in pre-cleared tissue, but easily visible after clearing. (D) CTB conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 or 594 was injected into each eye and a 700 μm frontal section of P5 brain was cleared with ClearT. Optical slices at 250 μm, 450 μm and 600 μm below the tissue section surface are shown (from 71 images, 10 μm steps). Both CTB labels were observable, though deeper, in cleared dLGN compared with the same tissue before clearing. Scale bars: 1 mm in C (top); 100 μm in A and bottom of C,D (bottom); 10 μm in B.
