Fig. 5.
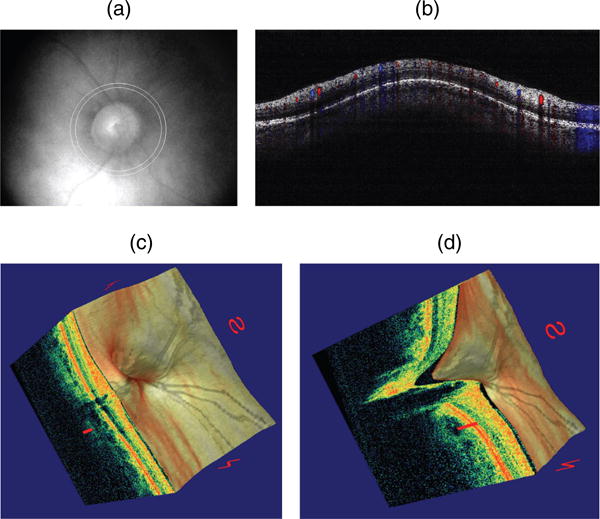
Doppler optical coherence tomography. (a) Fundus photograph showing the double circular pattern of the optical coherence tomography (OCT) beam scanning across retinal blood vessels emerging from the optic disc. (b) Color doppler OCT image showing the unfolded cross-section from a circular scan. Arteries and veins could be distinguished by the direction of flow as determined by the signs (blue or red color) of the Doppler shift. (c) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the optic nerve head showing the retinal layers. (d) Section of the three-dimensional reconstruction of the optic nerve head showing cupping.
