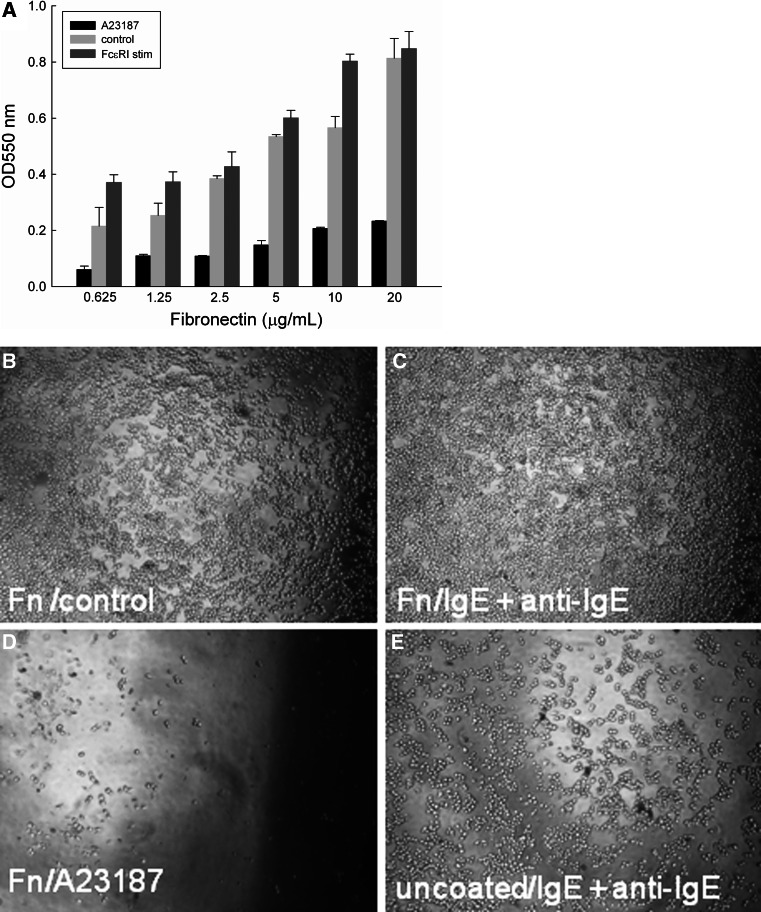
Fig. 3.
a Attachment of RBL-703/21 cells to FN. Different concentrations of FN (0.625–20 μg/mL) were used for coating, cells were activated with 1 μg/mL A23187, 2 μg/mL anti-IgE, or left untreated (control). 120 min after activation, cells were washed three times and the amount of adherent cells was quantified by a colorimetric assay using crystal violet. Data expressed are mean ± SD from triplicate determinations. Representative of three independent experiments with comparable results. Multiple comparison for two variables was obtained with a two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test to assess the statistical significance of FN and the type of stimulation for cell attachment/detachment. There was a highly significant effect of FN (F(5,32) = 163.458, p < 0.001) and the type of stimulation (F(2,36) = 611.867, p < 0.001) on cell attachment. b–e ×50 Light microscopy magnification of RBL 703-21 cells, after 2-h binding to 20 μg/mL FN without stimulation (b), activation with 2 μg/mL anti-IgE with FN (c), or activation with 1 μg/mL A23187 with FN (d), or activated with 2 μg/mL anti-IgE without FN coating (e)