Figure 1.
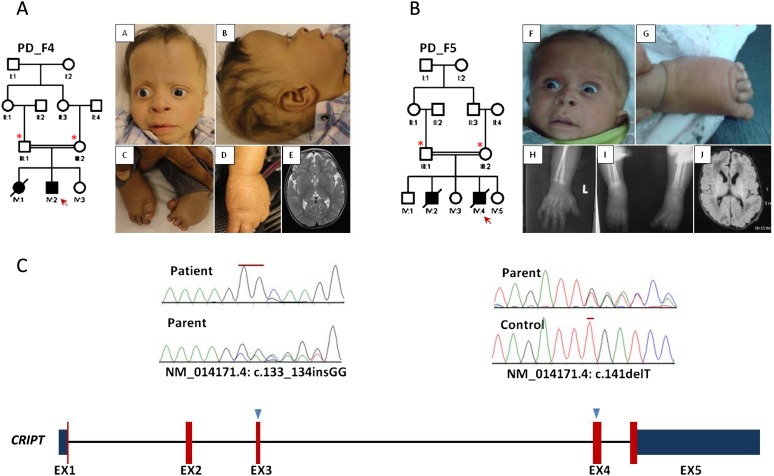
Identification of a novel PD syndrome linked to CRIPT. (A,B) Pedigrees and clinical photographs of PD_F4_IV:2 and PD_F5_IV:4, respectively. The index is indicated by a red arrow, and asterisks denote individuals whose DNA was available for analysis. Note the strikingly similar clinical appearance (high forehead, mild proptosis, anteverted nares, flat nasal bridge, hypoplastic digits and talipes). Please also note the mottled hypopigmentation in PD_F4_IV:2. (C) Diagram of CRIPT (numbers indicate the number of exons, red color represents the coding exons while blue is the 5′ and 3′ UTR, and triangles indicate the sites of the mutations). (Upper panel) Sequence chromatogram showing the homozygous frameshift insertion in PD_F4_IV:2 and the heterozygous frameshift deletion in the parent of PD_F5_IV:4 (mutations are denoted by red lines).