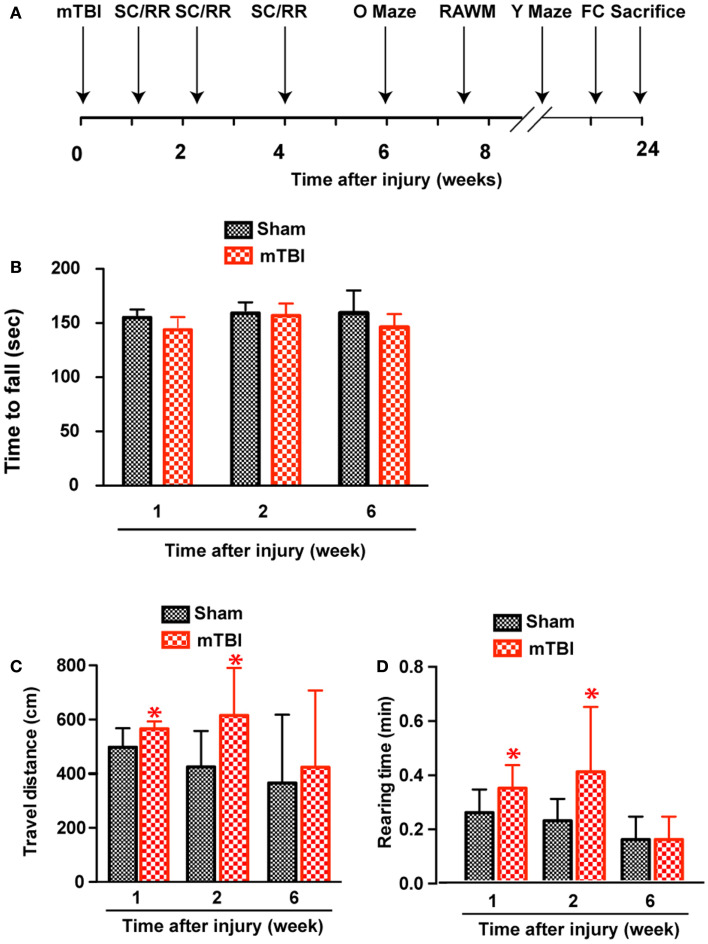
Figure 3.
Increased exploratory behavior after repetitive mTBI without significant motor defects. Wild-type C57BL/6J mice (male, 3 months of age, body weight 24.14 ± 3.18 g) received three mild impacts (mTBI) or underwent sham procedures (sham). (A) Schematic showing schedule of behavioral tests employed in this study at the following time points after injury: SmartCage (SC) and Rota-Rod (RR), 1, 2, and 6 weeks; Elevated zero maze (O maze), 6 weeks; radial arm water maze (RAWM), 7–8 weeks; and Y-maze and fear conditioning (FC) 23–24 weeks. (B) Motor function was tested by a Rota-Rod apparatus. No difference between the mTBI and sham groups was observed at any time points. (C,D) Exploratory behavior was monitored for 5 min in the SmartCage. Mice exposed to mTBI traveled significantly longer distance (C) and reared significantly more (D) than the sham group at 1 and 2 weeks after injury. n = 8 (sham) and 15 (mTBI) mice/group. Mean ± SD; *P < 0.05, repeated measures ANOVA.