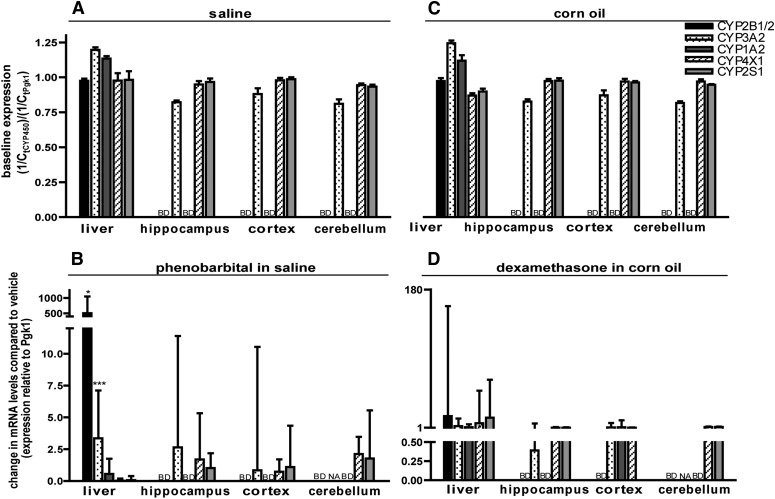
Fig. 3.
P450 expression profiles in the brain of adult male Sprague-Dawley rats. Rats were treated for 3 consecutive days with either saline (5 ml/kg/day, i.p.) (A) or an equal volume of PB in saline (102 mg/kg/day, i.p.) (B), or for 4 consecutive days with either CO (5 ml/kg/day, i.p.) (C) or an equal volume of DEX in CO (50 mg/kg/day, i.p.) (D). Tissues were harvested 24 hours after the last injection and P450 mRNA quantified by quantitative (real-time) polymerase chain reaction. (A and C) Baseline P450 expression determined by normalizing fractional amplification (Ct) values for CYP transcripts in vehicle control tissues to Ct values for phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (Pgk1) in the same sample. (B and D) Change in expression of the target gene in PB- or DEX-treated animals relative to control (saline for PB and CO for DEX). Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E. (n = 3 except for PB-treated cerebellum, in which n = 2). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, significantly different from vehicle controls as determined by automated randomization and bootstrapping tests (REST 2009 software). BD, below detection limit; NA, not available because of low amplification efficiency.