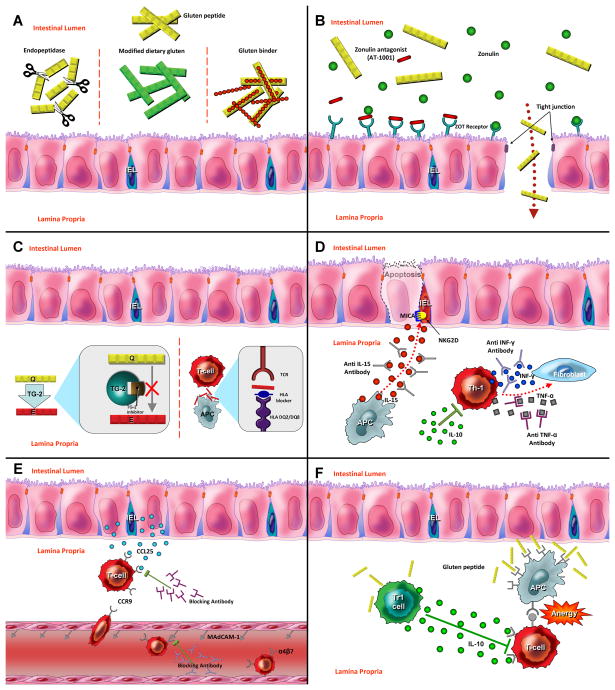
Figure 1. New therapeutic approaches for celiac disease.
(A) Detoxification of gluten. Polymeric binders or endopeptidase enzymes act in the intestinal lumen to reduce immunogenicity of harmful gluten peptide. Non-toxic wheat strains lacking immunostimulatory gluten peptides can be an alternative for gluten-free diet. (B) Permeability Modulation. Zonulin antagonist (AT-1001) binds to ZOT Receptors and reduces mucosal permeability by prevention of tight junction impairment. (C) Antigen Presentation Blockade. Inhibition of adaptive immunity by use of TG2 inhibitors and HLA-blocking compounds (D) Cytokine Therapy. Monoclonal antibodies against inflammatory cytokines such as INF-gamma, TNF-alpha and IL-15 reduce mucosal injury in celiac disease. Regulatory cytokines such as IL-10 can be used for suppression of Th1 activation. (E) Inhibition of T cell recruitment. Anti adhesion compound such as anti α4 antibodies lock immune cell migration to the intestinal tissues. (F) Oral tolerance induction. Low dose tolerance is driven by regulatory T cells via IL-10 secretion. High dose of antigen mediates lymphocyte anergy via interaction between effector T lymphocyte and Antigen presenting cells.