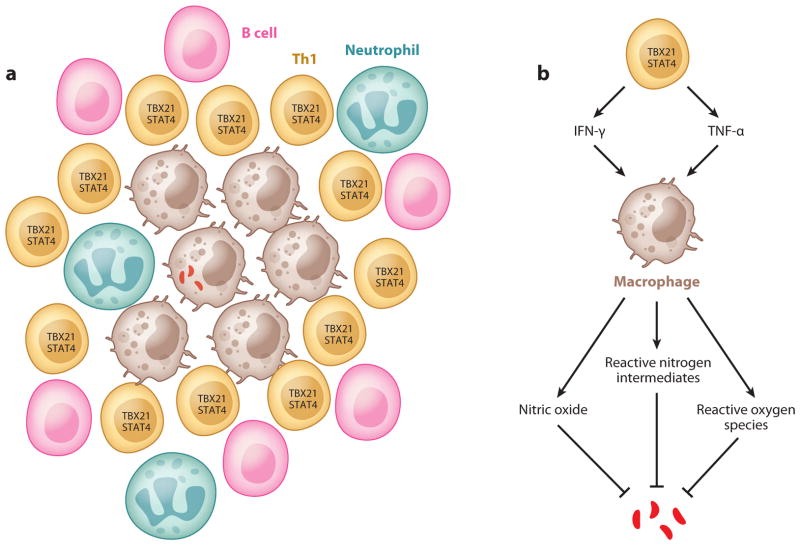
Figure 2.
Th1 cells and granuloma formation. (a) Schematic representation of granuloma structure: An infected macrophage is surrounded by many cell types such as uninfected macrophages, Th1 cells, B cells, and neutrophils. (b) Functions of Th1 cells in tuberculosis: Th1 cells activate macrophages via cytokines such as TNF-α and IFN-γ. Activated macrophages kill bacteria through nitric oxide, reactive nitrogen intermediates, and reactive oxygen species (see text for details).