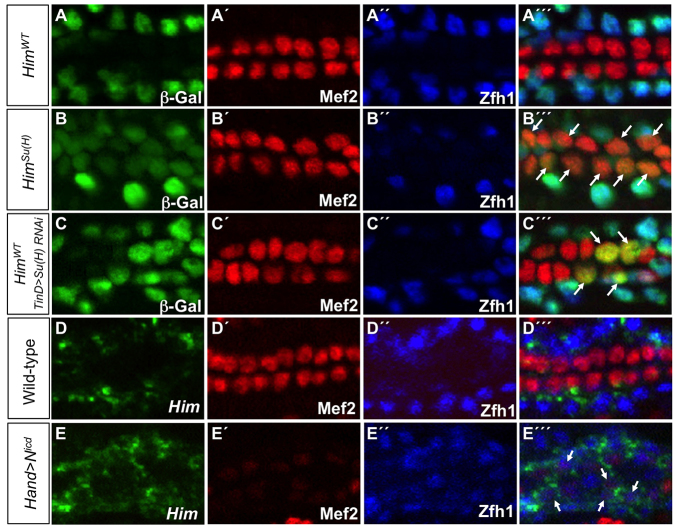
Fig. 7.
Su(H) discriminates between PC and CC enhancer activities. (A-C′′) lacZ reporter gene activity (β-galactosidase, green) driven by relevant Him enhancers in indicated genotypes. All CCs express Mef2 (red) whereas PCs are marked by Zfh1 (blue). (A-A′′) The wild-type Him enhancer (HimWT) is active only in the Zfh1-expressing PCs. (B-B′′) When the Su(H) binding site is mutated in the Him enhancer [HimSu(H)], the reporter is still active in Zfh1-expressing PCs but is de-repressed in Mef2-positive CCs (arrows). (C-C′′) Knockdown of Su(H) with dorsal mesoderm-targeted RNAi driven by the TinD-GAL4 driver induces ectopic HimWT enhancer-driven β-galactosidase reporter activity in CCs (arrows). (D-E′′) Fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis of stage 16 embryos for Him mRNA (D,E) and antibody analysis for Mef2 (D′,E′) and Zfh1 (D′,E′) of the indicated genotypes. (D-D′′) Him mRNA is restricted to the Zfh1-expressing PCs of the wild-type heart. (E-E′′) Overexpression of Nicd in all cells of the heart driven by the Hand-GAL4 driver leads to ectopic Him mRNA being expressed in the weakly Mef2-expressing CCs (arrows).