Figure 1.
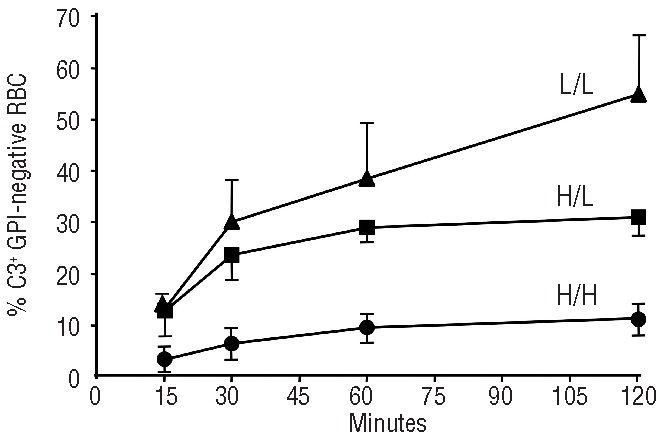
The CR1 genotype is a major determinant of the rate of in vitro C3 binding to GPI-negative red cells. In each patient this time course experiment was carried out twice. H/H: homozygotes for the high expression allele of the CR1 HindIII RFLP polymorphism. L/L: homozygotes for the low expression allele of the CR1 HindIII RFLP polymorphism. H/L= heterozygotes for the CR1 HindIII RFLP polymorphism. The standard deviation is shown for each experimental point. When eculizumab-containing sera were added to red cells, the slope of novel C3 binding to GPI-negative red cells was significantly different depending on the CR1 genotype. For the comparison of H/H (n=6) vs. H/L (n=3), P=0.0425; for the comparisonvs H/L (n=3) vs. L/L (n=2), P=0.0173; for the comparison H/H (n=6). L/L (n=2), P<0.0001. Given a certain CR1 genotype these differences were not the result of eculizumab treatment: indeed, in three patients with the H/H genotype who were on eculizumab, the rate of C3 binding to GPI-negative red cells was very similar to that seen in three patients with the H/H genotype who were not on eculizumab (P=0.87).
