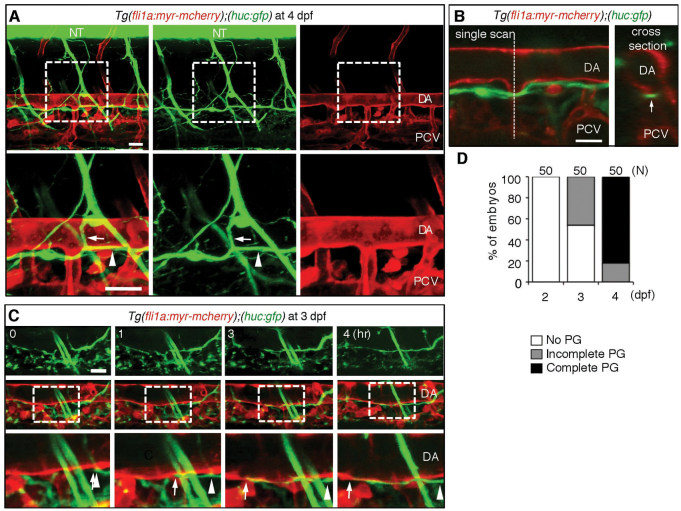
Fig. 1.
Neuronal axons extend beneath the dorsal aorta in zebrafish. (A) 3D-rendered confocal stack fluorescence images (lateral view) of an Tg(fli1a:myr-mcherry);(huc:gfp) embryo at 4 dpf. Left column, merged images; center column, GFP images; right column, mCherry images. Anterior is to the left. Arrows and arrowheads indicate branches of motoneuron axons and those found beneath the DA. Lower panels show magnifications of the boxed areas in upper panels. (B) Left, a single scan confocal image from the stack shown in A. Right, a cross-section image of the stacked image shown in A at the level indicated by the dashed line in the left panel. Arrow denotes a single fascicle of axons. (C) 3D-rendered confocal time-sequential stack images of an Tg(fli1a:myr-mcherry);(huc:gfp) embryo. Elapsed time (hours) from the start point of time-lapse imaging (3 dpf) is indicated. Top panels, GFP images; middle panels, merged images of GFP and mCherry; bottom panels, enlarged images of boxed regions of middle panels. Arrows and arrowheads indicate the tip of the axon and the location of the tip when starting to extend, respectively. (D) Quantitative analyses of the parallel growth (PG) of axons with the DA at the time points indicated. ‘Complete’ indicates the complete continuity of the axon between the region above the rostral part of the yolk tube and that above the caudal part of the yolk tube. The number of embryos observed is indicated at the top. Scale bars: 25 μm. DA, dorsal aorta; NT, neural tube; PCV, posterior cardinal vein.