Figure 1.
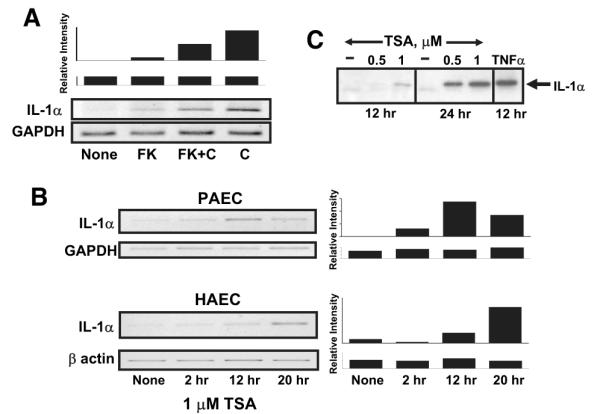
IL-1α expression is activated by complement and regulated by histone deacetylase in endothelial cells. Expression of IL-1α was evaluated in confluent cultures of porcine (PAEC) or human (HAEC) aortic endothelial cells. A, Complement-stimulated IL-1α expression requires calcineurin. Porcine aortic endothelial cells were left untreated (none) or were treated with 100 nmol/L FK506 (FK) for 2 hours to inhibit calcineurin. The cells were then were exposed to 12% human serum for 4 hours to activate complement (indicated as C). Total cellular RNA was prepared and analyzed for IL-1α mRNA using quantitative RT-PCR. The samples were also analyzed for GAPDH as a control for equal mRNA loading and quality. The representative gels shown at the bottom are representative of 3 separate experiments. The densitometry scan bar graph at the top reflect IL-1α/GAPDH mRNA levels. B, IL-1α expression is regulated by histone deacetylase. Confluent cultures of porcine or human aortic endothelial cells were treated with 1 μmol/L trichostatin A (TSA) for various periods of time, as shown, to inhibit histone deacetylase. Total cellular RNA was prepared, and expression of IL-1α mRNA or control GAPDH or β-actin mRNA was evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR as described above. C, Porcine aortic endothelial cells were treated with 0.5 or 1.0 μmol/L trichostatin A or with the drug vehicle alone for 12 or 24 hours. A positive control sample was stimulated with 10 nmol/L TNFα. Secretion of IL-1α into cell culture supernatants was analyzed from equal volumes of supernatant by immunoblot using anti-porcine IL-1α antibodies. The results show that complement or an inhibitor of histone deacetylase induces IL-1α gene expression in endothelial cells.
