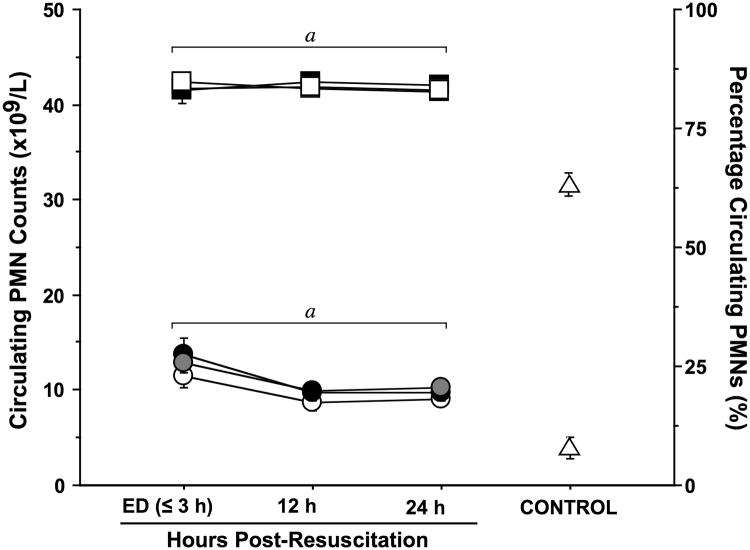
Fig. 1. TBI induces sustained neutrophilia.
Peripheral blood samples were collected in EDTA vacutainers from healthy controls (n=20) and trauma patients resuscitated with NS (n=39), HSD (n=22), or HS (n=22) at the time of emergency department (ED) admission (≤3 h post-resuscitation) and 12 and 24 h post-resuscitation. Both the percentage (square symbols) of neutrophils among all white blood cells and the concentration (circles) of neutrophils (PMNs) in the peripheral blood were elevated relative to levels in healthy controls (triangles) throughout the sampling period, as determined by a Beckman Coulter Hematology Analyzer. Statistics: ap < 0.05 vs. age-matched healthy controls by ANOVA.