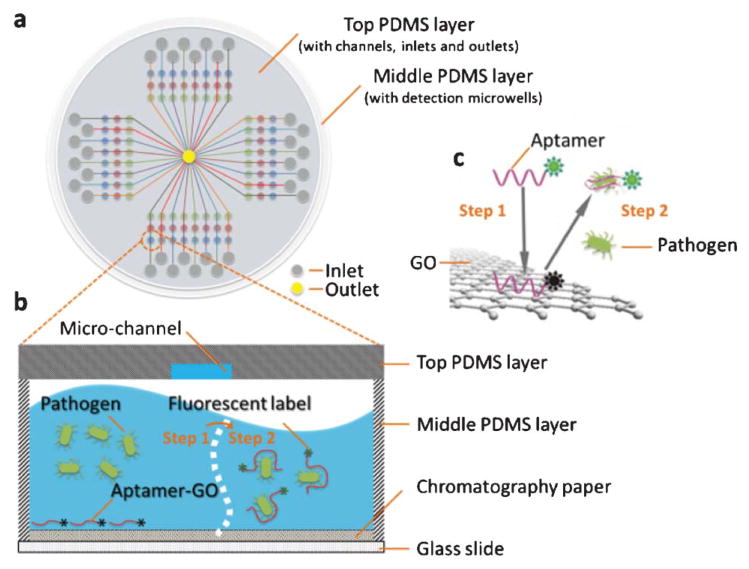
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the PDMS/paper hybrid microfluidic system for one-step multiplexed pathogen detection using aptamer-functionalized GO biosensors (not drawn to scale). (a) Microfluidic biochip layout, (b) and (c) illustrate the principle of the one-step ‘turn-on’ detection approach based on the interaction among GO, aptamers and pathogens. Step 1: when an aptamer is adsorbed on the GO surface, its fluorescence is quenched. Step 2: when the target pathogen is present, the target pathogen induces the aptamer to be liberated from GO and thereby restores its fluorescence for detection.