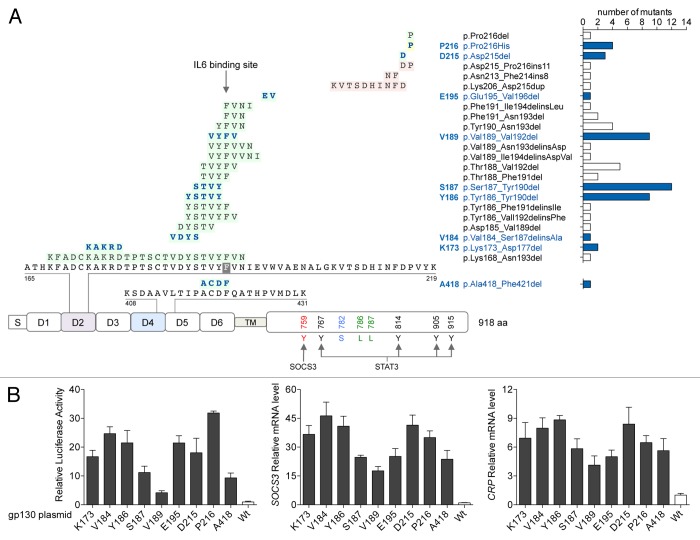
Figure 1. Gain-of-function mutations of gp130 in IHCA. (A) Spectrum of somatic mutations affecting interleukin-6 (IL-6) signal transducer (IL6ST) in human inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma (IHCA) samples (n = 256). DNA sequencing of IL6ST of was performed to identify the resultant alterations in gp130, including in-frame deletions (in green), insertions or deletions (in pink) and amino acid substitutions (in yellow) occurring in the different domains of the protein (S, signal peptide; D1-D6, extracellular domains; TM, transmembrane domain). Right, occurrence of the different mutants with their official nomenclature. Mutants reproduced by site-directed mutagenesis (for functional analysis) are in blue. (B) Plasmids engineered to express either IHCA-associated gp130 mutants or wild-type (WT) gp130 were co-transfected into Hep3B cells (n = 3) along with a STAT3-driven luciferase (Luc) reporter. STAT3 activation (left) was measured by luciferase activity 6 h after serum starvation. Shown are the means ± SD luciferase activity. Quantitative PCR was also used to examine the effects of expressing mutant gp130 on SOCS3 (center) or CRP (right) mRNA expression levels in comparison to WT gp130. Shown is the mean ± SD of the normalized mRNA levels in mutants relative to WT gp130 controls (1-fold).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.