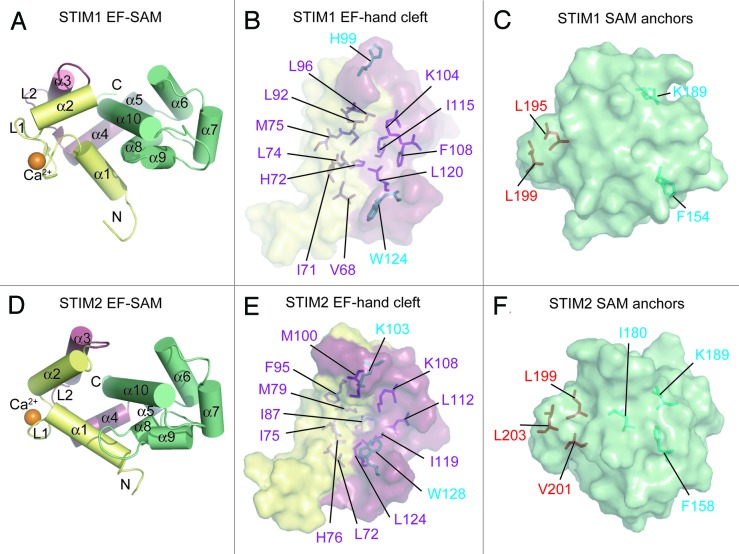
Figure 2. Ca2+-loaded STIM1 and STIM2 EF-SAM structural features. (A) Compact α-helical fold of Ca2+-loaded STIM1 EF-SAM. The 10 α-helices making up the compact fold of EF-SAM are labeled. (B) The STIM1 EF-hand hydrophobic cleft composition. The hydrophobic amino acids which create the non-polar cavity are shown as sticks (purple) on the surface depiction of the EF-hand domain. Residues which do not contribute to the cleft, but align with hydrophobic components of the STIM2 EF-hand cleft are colored cyan. (C) The STIM1 SAM domain hydrophobic anchors which pack into the hydrophobic cleft. The SAM domain is shown as a surface representation with hydrophobic anchor residues depicted as sticks (red). Residues which do not contribute to the hydrophobic core, but align with residues that are buried non-polar components of the STIM2 SAM domain are colored cyan. (D) Compact α-helical fold of Ca2+-loaded STIM2 EF-SAM. The 10 α-helices making up the compact fold are labeled. (E) The STIM2 EF-hand hydrophobic cleft composition. The hydrophobic residues which create the non-polar cavity are shown as sticks (purple and cyan) on the surface representation of the EF-hand domain. (F) The STIM2 SAM domain is shown as surface representation with hydrophobic anchor resides depicted as sticks (red). Residues which contribute to the hydrophobic core of the STIM2 SAM, but are not structurally conserved in the STIM1 SAM domain are shown in cyan. In (A–F), the domain color is consistent with Figure 1 and Ca2+ is shown as orange spheres; N and C denote amino and carboxy termini, respectively. Images were created with 2K60.pdb and 2L5Y.pdb coordinates for STIM1 and STIM2 EF-SAM, respectively.31,55

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.