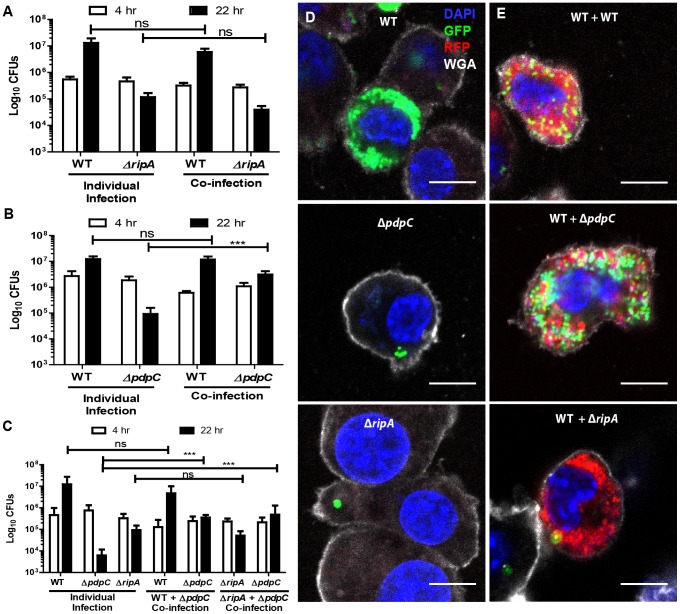
Figure 5. Functional trans-complementation via bead-bound bacteria complements intracellular proliferation of ΔpdpC but not ΔripA.
(A) Kanamycin resistant wild-type LVS or hygromycin resistant ΔripA were individually or co-inoculated into J774 cells and assayed for intracellular proliferation at 4 and 22 hours post inoculation. (B) Kanamycin resistant wild-type LVS or hygromycin resistant ΔpdpC were individually or co-inoculated into J774 cells and assayed for intracellular proliferation at 4 and 22 hours post inoculation. (C) Kanamycin resistant wild-type LVS, kanamycin resistant ΔripA or hygromycin resistant ΔpdpC were individually or co-inoculated into J774 cells and assayed for intracellular proliferation at 4 and 22 hours post inoculation. Results are from 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate or triplicate. Bar graphs represent the mean +/− the standard deviation. (D) Representative fluorescence micrographs of J774 cells inoculated for 22 hours with GFP wild-type, GFPΔpdpC or GFPΔripA bacteria attached to beads. (E) Representative fluorescence micrographs of J774 cells inoculated with beads bound to DsRed LVS and either GFP WT, GFPΔpdpC or GFPΔripA. Blue represents the nucleus (DAPI), green represents the indicated GFP LVS mutants, red represents DsRed wild-type LVS, and white represents the plasma membrane stain wheat germ agglutinin (WGA). All scale bars represent 10 µm. All samples were bound to beads prior to infection. Not significant (ns), p>.05, * p<0.05, ***p<0.005.