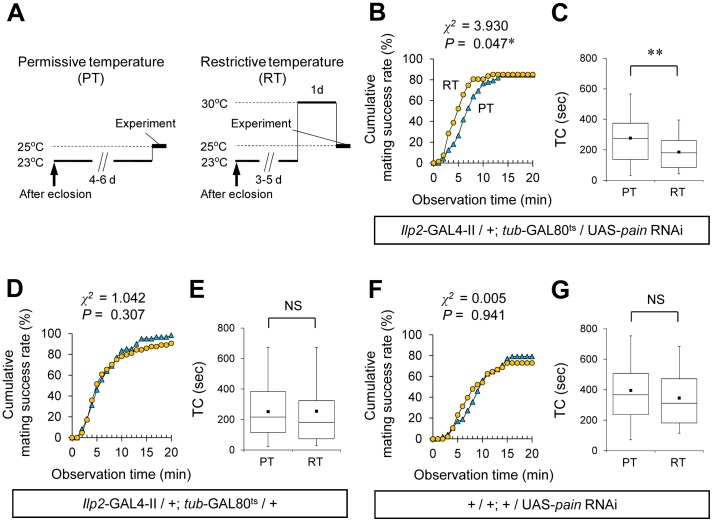
Figure 6. Conditional knockdown of pain expression in IPCs enhances female sexual receptivity.
(A) Schematic diagram of temperature shift experiments. Animals were kept at 25.0±0.5°C during the embryonic, larval and pupal stages. Two temperature shift experiments (PT and RT) were performed as follows: PT, virgin females were collected and kept at the PT (23.0±0.5°C) until just before the start of experiments; RT, virgin females were collected and kept at the PT until 1 day before experiments, then they were kept at the RT (30.0±0.5°C) until just before the start of the experiments. In both PT and RT, mating behaviors were observed at 25.0±0.5°C. (B, D, F) Cumulative mating success rate (%) in Ilp2-GAL4-II/+; tub-GAL80ts/UAS-pain RNAi (B), Ilp2-GAL4-II/+; tub-GAL80ts/+ (D), and UAS-pain RNAi/+ (F) females. Virgin females of the indicated genotypes and wild-type males were used. The observation period was 20 min. 48–72 pairs were observed for each genotype. A log-rank test was used for comparison between PT (blue triangles) and RT (yellow circles). *, P<0.05. (C, E, G) Time to copulation (TC) in Ilp2-GAL4-II/+; tub-GAL80ts/UAS-pain RNAi (C), Ilp2-GAL4-II/+; tub-GAL80ts/+ (E), and UAS-pain RNAi/+ (G) females. N = 35–61 in each genotype. A Mann-Whitney U test was used for pairwise comparisons. **, P<0.01; NS, not significant.