Figure 8.
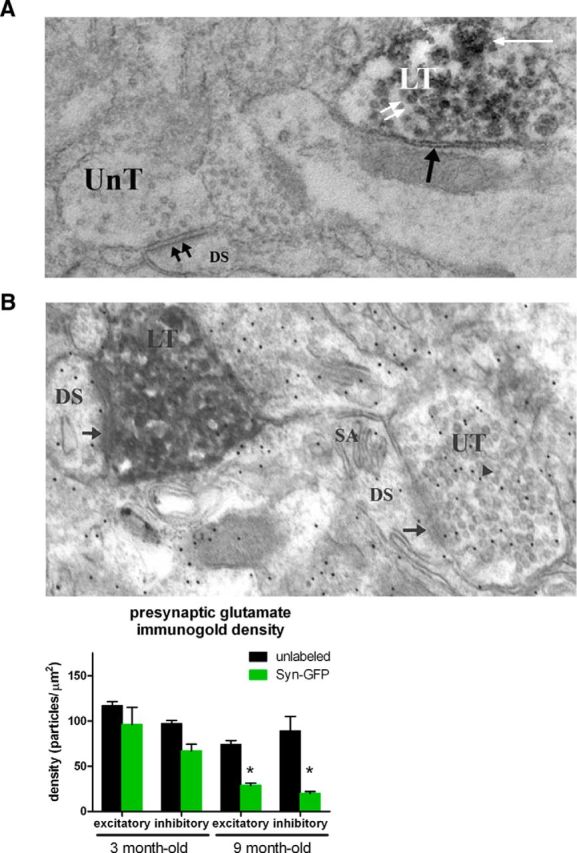
Electron microscopy of terminals. A, Electron photomicrograph showing unlabeled terminal (UnT) making an asymmetrical (double black arrows) synaptic contact onto a dendritic spine (DS), indicating that the synapse is excitatory. Also in the field is a DAB-labeled terminal (LT) making a symmetrical (inhibitory) synaptic contact (single black arrow) and containing a perivesicular (double white arrows) and granular (single white arrow) pattern of labeling. B, Top, Electron photomicrograph showing an unlabeled nerve terminal (UT) making an asymmetrical synaptic contact (arrow) onto a DS containing a spine apparatus (SA). Within the unlabeled nerve terminal are numerous 12 nm gold particles (arrowhead) indicating the location of an antibody against glutamate. There is also a DAB/α synuclein-GFP-labeled nerve terminal (LT) making an asymmetrical synaptic contact (arrow) onto a DS. Bottom, Group data from animals of two different age groups, 3 and 9 months old, showing a significant decrease in presynaptic glutamate levels in 9-month-old Syn-GFP-positive excitatory (asymmetrical) and inhibitory (symmetrical) nerve terminals.
