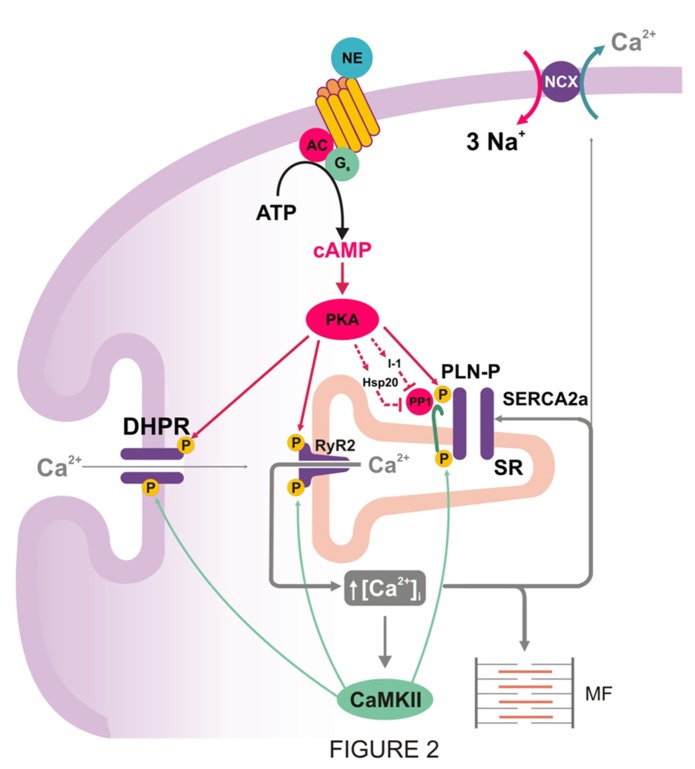
FIGURE 2.
PKA mediated increase in cytosolic Ca2+ and inhibition of PP1: two prerequisites for CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of PLN during β1-adrenergic stimulation. PKA-dependent phosphorylation of Ca2+ handling proteins, particularly L-type Ca2+ channel and PLN, produces an increase in cytosolic Ca2+ that is necessary to activate CaMKII and produce CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation. PKA also increases inhibitor-1 and Hsp20 phosphorylation, amplifying the stimulatory effects of β1–adrenergic stimulation on SR Ca2+-transport, relaxation, and contractility.