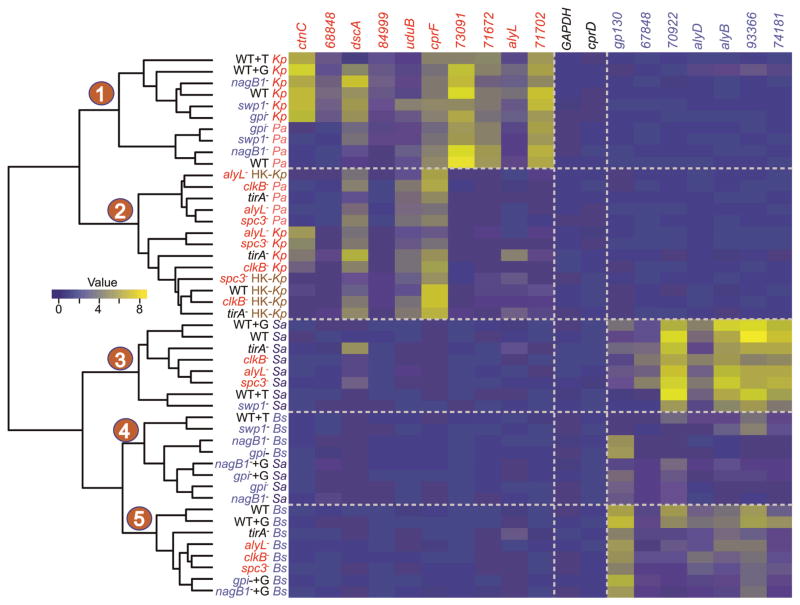
Figure 3. Changes in the transcriptional landscape in mutants with defective growth phenotypes.
The heat map represents the patterns of change in normalized mRNA levels (qRT-PCR) of selected genes in different D. discoideum strains (yellow, higher relative abundance; blue, lower relative abundance). The mRNA levels of each gene (log2 scale) were normalized to the mRNA levels determined for the histone H3a gene. Each row represents a wild type or mutant strain in one bacterial growth condition. Each column represents the relative abundance of a given gene; ctnC and 68848 are K. pneumoniae-specific genes, dscA to 71702 (DDB_G0271702) are Gram(−)-enriched genes, GAPDH and cprD are control genes, and gp130 to 74181 (DDB_G0274181) are Gram(+)-enriched genes [37]. The dendrogram depicts the Euclidean distances between the different D. disoideum strains (wild-type or mutant) grown on different bacterial species: wild-type AX4 (WT); K. pneumoniae (K.p.); Heat-killed K. pneumoniae (HK-K.p.); P. aeruginosa (P.a.); S. aureus (S.a.); B. subtilis (B.s.); G, glucose; and T, tunicamycin. The major divide in the clustering is evident between strains grown on Gram(+) and Gram(−) bacteria. D. discoideum mutants that are defective in growth on Gram(−) bacteria and the tirA− mutant cluster together when grown on live Gram(−) bacteria, or on Heat-killed K.p., along with wild-type grown on heat-killed K.p. (clade 2). D. discoideum mutants that are defective in growth on Gram(−) bacteria and the tirA− mutant cluster together with wild-type D. discoideum when grown on Gram(+) bacteria (clade 3 and 5). Mutant strains nagB1− and gpi that are defective in growth on Gram(+) bacteria cluster together when mixed with Gram(+) bacteria (clade 4), but cluster with the wild type when grown on Gram(−) bacteria (clade 1).