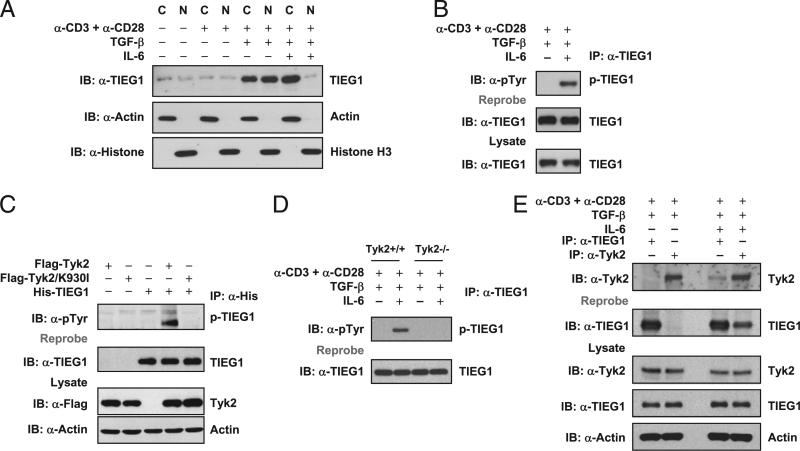
FIGURE 1.
IL-6–Tyk2 pathway-mediated phosphorylation regulates TIEG1 nuclear localization and Treg/Th17 differentiation. A, Naive CD4+CD25– T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 in the presence of TGF-β (5 ng/ml) alone or TGF-β (5 ng/ml) plus IL-6 (20 ng/ml). The nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were immunoblotted with anti-TIEG1 Ab. The membranes were reprobed with anti-histone H3 and anti-actin Ab. C, cytoplasmic; N, nuclear. B, CD4+CD25– T cells were treated as in A. Endogenous TIEG1 from total-cell lysates was immunoprecipitated with anti-TIEG1 Ab and immunoblotted with anti–phos-tyrosine Ab. Blots were reprobed using anti-TIEG1 Ab, p-TIEG1, or tyrosine-phosphorylated TIEG1. C, 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding His-TIEG1, Flag-Tyk2, or Flag-Tyk2/K930I, alone or in combination, for 24 h. TIEG1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-His Ab and immunoblotted with anti–phos-tyrosine Ab. Blot was stripped and reprobed with anti-TIEG1. The amount of Tyk2 in total-cell lysates was determined by immunoblotting. Actin was used as an equal loading control. D, Naive CD4+CD25– T cells isolated from Tyk2+/+ and Tyk2–/– mice were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 in the presence of TGF-β (5 ng/ml) alone or TGF-β (5 ng/ml) plus IL-6 (20 ng/ml). TIEG1 was immunoprecipitated using anti-TIEG1 Ab and immunoblotted using anti–phos-tyrosine Ab. E, TIEG1 interacts with Tyk2 in primary CD4 T cells. CD4+CD25– T cells were stimulated with TGF-β or TGF-β plus IL-6, as described above. Endogenous TIEG1 or Tyk2 was immunoprecipitated with corresponding Abs and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Tyk2. The same blot was stripped and reprobed with anti-TIEG1. The amount of TIEG1 and Tyk2 in total-cell extracts was determined by Western blotting. Actin was used as an equal loading control.