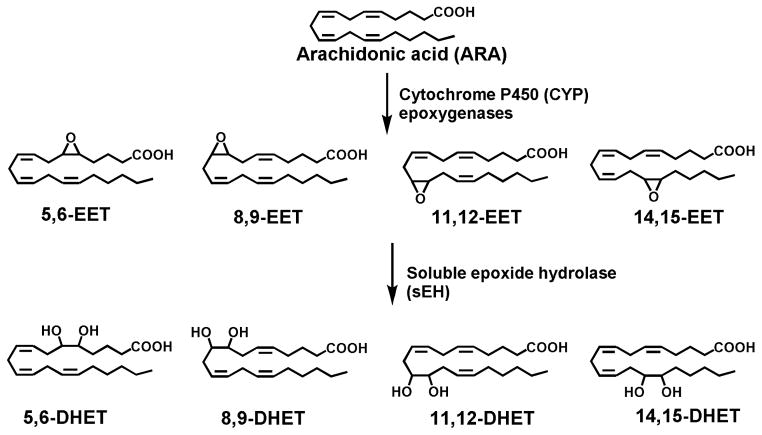
Fig. 1.
The metabolism of arachidonic acid by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases (largely CYP2C and CYP2J) leads to the formation of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) including four regioisomers of 5,6-, 8,9-, 11,12- and 14,15-EET. EETs are further metabolized by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) to form the fatty acid diols termed dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs) which are usually less-active or inactive.