Table 3.
De novo N-terminal motif search results for the pathogen-associated protein clusters in F. graminearum
| Motif logo and regular expression | Prevalence in cluster | E-value | Average start position in protein | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster C4 |
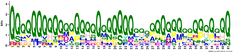 |
10 sites |
3.5e-31 |
143 |
Domain seems widespread throughout eukaryotic kingdom. |
| Q[QS]QQQQQ[QH]QQ[QDM][QAP][QP]Q[QH]QQ[QM][QN]Q[QS]QQ[QL][QH]Q[QAP]QQ[QA][QAP][QM][QL][QP]Q[QP][QH][QP][QL][QH]Q | |||||
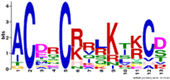 |
13 sites |
8.0e-24 |
56 |
Domain seems restricted to fungal kingdom, large number of hits predominantly to the Ascomycota. Some protein hits are annotated as fungal transcriptional regulatory proteins or GTP binding protein. |
|
| AC[DE]RC[RK]R[LR]K[IT][KR]C[DS] | |||||
 |
6 sites |
5.1e-03 |
48 |
Domain seems restricted to fungal kingdom, large number of hits predominantly to the Ascomycota. Some protein hits are annotated with fungal transcriptional regulatory function. Weak Pfam domain annotation as zinc cluster. |
|
| CSRCV[KR]xKLDC[DE]Y | |||||
| Cluster C5 |
 |
6 sites |
9.2e-03 |
4 |
Domain seems widespread throughout eukaryotic kingdom. There are weak similarities to zinc-finger protein domain. |
| MCVxV[HT]KDITC[PS]TC | |||||
| Cluster C8 |
 |
37 sites |
9.3e-91 |
15 |
Motif is adjacent to predicted signal peptide cleavage site. Domain is restricted to pathogenic Fusarium genomes in our search. |
| [AL][LA]Axx[AV]xA[GS]PC[KR]PSS | |||||
 |
8 sites |
1.6e-29 |
47 |
Search converged after three iterations. Domain is restricted to F. graminearum, F. oxysporum, F. solani and the cereal pathogen G. graminicola. |
|
| WCITY[LE]STYL[VA][PA][VI]SN | |||||
| Cluster C12 |
 |
11 sites | 2.4e-16 | 11 | Domain restricted to fungal kingdom, hits are predominantly to Ascomycota including a large number of pathogens, e.g. S. nodorum. Weak hit to PRANC domain, which is found at the C-terminus of Pox virus proteins. L-P-x-E motif is also found in F-box like domains. |
| FH[PL]F[SL]RLPPE[LIV]RL[MQ]I[WY]RHALT |
We report motifs in F. graminearum which are distinct from convential signal peptides and which are conserved in more than 5 sequences and occur within the first 150 amino acids to identify potential novel signalling, subcellular targetting or uptake motifs.
