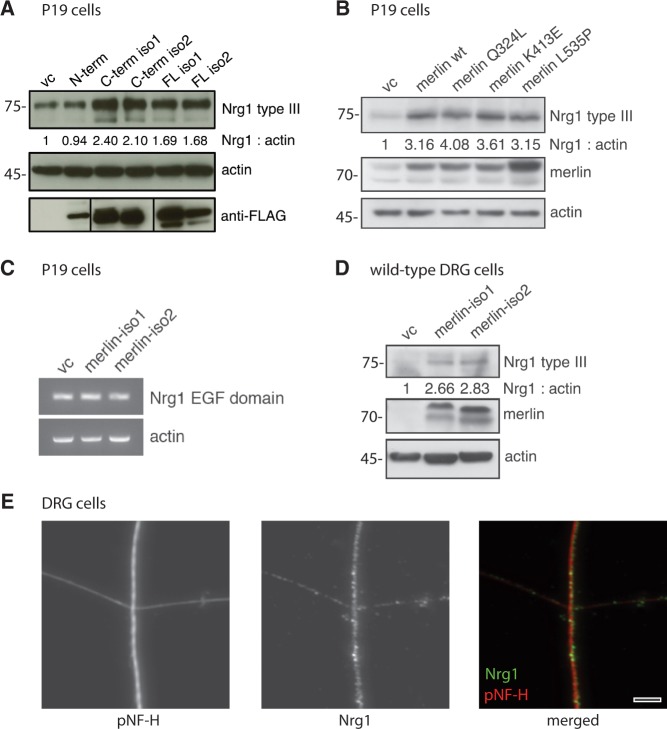
Figure 3.
Merlin overexpression in vitro induces NRG1 type III expression. (A) Immunoblot of P19 cell lysates after transfection of different FLAG-tagged merlin fragments. Transfection of empty vector was used as control (vc); actin indicates equal loading. Anti-FLAG staining shows transfection rate of each construct (n = 3). (B) Wild-type merlin isoform 1 (merlin wt) and merlin constructs bearing indicated C-terminal point mutations were transfected into P19 cells. Immunoblot shows NRG1 type III levels as well as merlin and actin as transfection and loading control, respectively (n = 2). Blot quantifications (density values) are depicted below respective lanes and are normalized to actin and transfection controls (vc). (C) Reverse-transcription PCR of P19 cell lysates following overexpression of merlin-iso1 or merlin-iso2 constructs. EGF domain-specific primers were used to detect Nrg1 transcripts. Actin was used as loading control (n = 3). (D) Immunoblot of lysates derived from primary dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cells after merlin overexpression in vitro (n = 3). Blot quantifications (density values) are depicted below respective lanes and are normalized to actin and transfection controls (vc). (E) Immunostaining of primary dorsal root ganglion cells shows localization of NRG1 (green) in axons of cultured dorsal root ganglions (4 days in vitro). Axons were stained for phosphorylated neurofilaments as an axonal marker (pNF-H, red). Scale bar = 5 µm. N-term = N-terminal fragment; C-Term = C-terminal fragment; FL = full length.