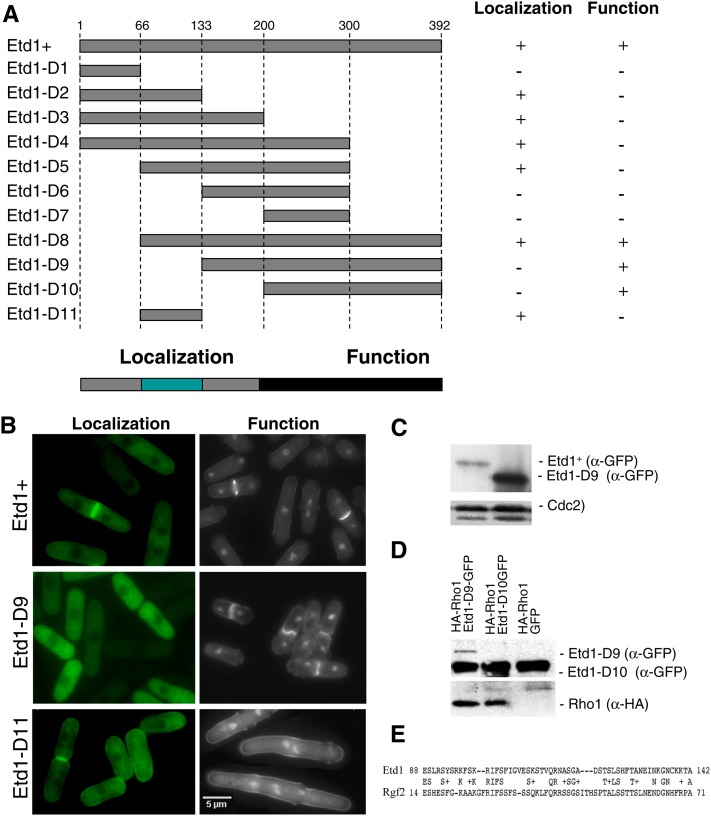
Figure 4.
Functional analysis of different Etd1 domains. (A) The indicated PCR-derived fragments of the Etd1-coding region (Etd1-D1 to Etd1-D10) were expressed in the pREP41x-GFP plasmid. Position of amino-acid residues flanking each Etd1 fragment is indicated. For cell localization assays, the GFP-fused constructs were expressed in wild-type cells in the absence of thiamine at 25°. For the functional complementation test, these constructs were expressed in the etd1Δ strain. Plasmids containing etd1Δ cells were grown at 37°, and the ability to rescue growth and division in this strain was assessed in the absence of thiamine at 25°. Etd1-truncated variants were classified as functional (+) or nonfunctional (−) according to their cell localization and complementation properties. The fragment containing the entire Etd1-coding region was used as control. Essential regions required for proper Etd1 cell localization and function are indicated. (B) Cell localization assay and functional complementation test of Etd1+ (control), Etd1-D9, and Etd1-D11 fragments. GFP fluorescence of wild-type cells expressing Etd1-GFP, Etd1-D9-GTP, or Etd1-D11-GTP constructs (left panels). DAPI and Calcofluor staining of etd1Δ cells under the expression of these constructs (right panels). (C) Western blot analysis of Etd1+ and Etd1-D9 (GFP-tagged). Cdc2 protein was used as a control. (D) Physical association of functional truncated variants Etd1-D9 and Etd1-D10 (GFP-tagged) and Rho1 (HA-tagged). Protein extracts prepared from cells expressing HA-Rho1 and Etd1-D9-GFP, Etd1-D10-GFP or GFP (negative control) were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies; the immunoprecipitates were run on SDS–PAGE gels and probed with anti-GFP and anti-HA antibodies. Western blots of total extracts were also probed with anti-GFP and anti-HA antibodies to check the levels of tagged proteins. (E) Sequence similarity between Etd1 and Rgf2 in a region that largely overlaps with the Etd1 localization domain.