Figure 1.
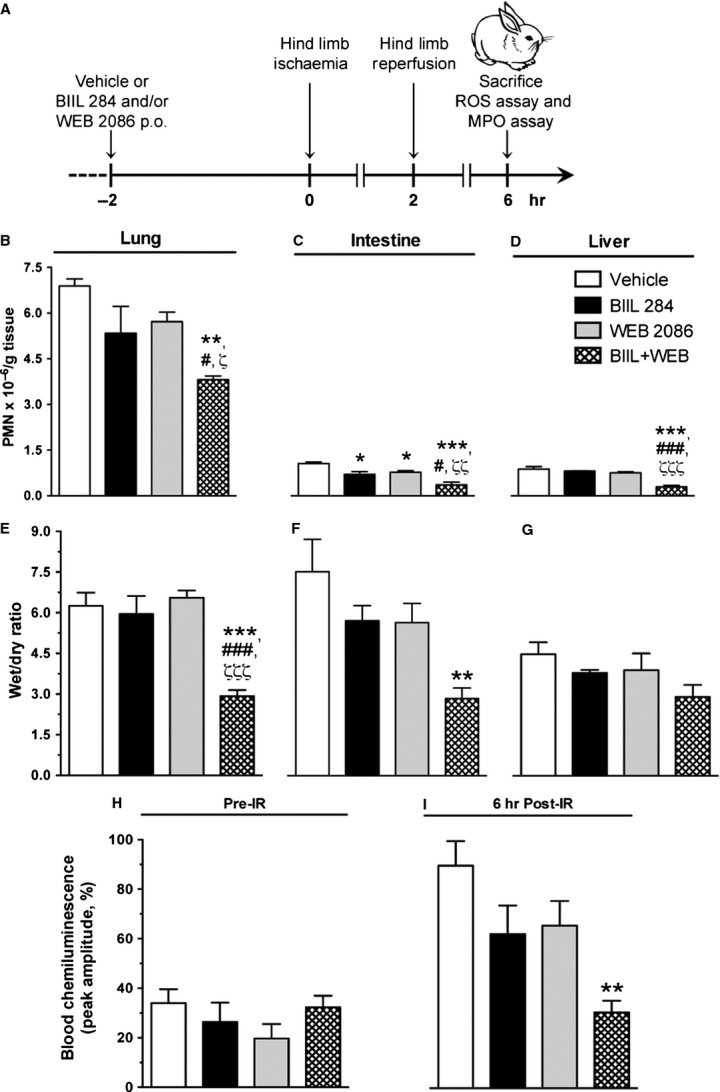
Effect of BIIL 284 and WEB 2086 on polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) recruitment and oedema to remote organs and whole blood chemiluminescence following hind limb I/R in rabbits. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental protocol involving the oral administration of BIIL 284 (0.01 mg/kg), WEB 2086 (10 mg/kg) or both drugs 2 hrs before subjecting rabbits to bilateral ischaemia of the lower limbs. The effect of single or combined drug administration on PMN recruitment to (B) lungs (left lobe), (C) intestine (jejunum) and (D) liver as assessed by myeloperoxidase assay. The effect of drugs on tissue oedema of (E) lungs (right lobe), (F) intestine and (G) liver as assessed by determining the wet/dry ratio. The effect of drug treatment on reactive oxygen species generation in whole blood stimulated by OpZ (H) before, and 6 hrs after I/R of lower limbs, as assessed by blood chemiluminescence. Data are the mean ± SEM obtained from four rabbits. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus water; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 versus BIIL 284; ζP < 0.05, ζζP < 0.01, ζζζP < 0.001 versus WEB 2086.
