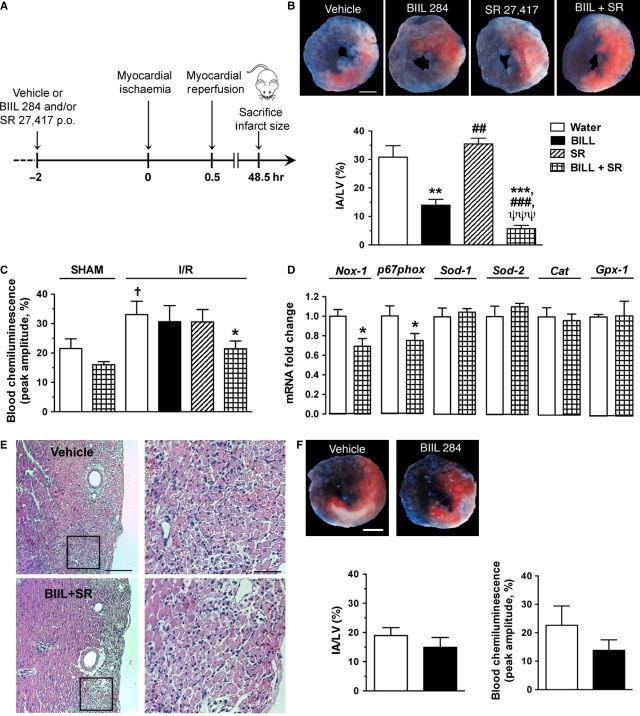
Figure 4.
BIIL 284 and SR 27417 reduced infarcted areas following myocardial I/R in wild-type (WT) mice. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental protocol involving the oral administration of BIIL 284 (0.1 mg/kg), SR 27417 (0.3 mg/kg) or both drugs 2 hrs before subjecting them to transient myocardial ischaemia following the occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery. (B) Representative photomicrographs of the mid-ventricular myocardium showing the area at risk [red staining including infarcted (white) tissue] and non-ischaemic (blue staining) section of left ventricle and a bar graph showing the effect of drug pre-treatment on infarct area (n = 5–7 WT mice per group); scale bar = 1 mm. (C) The effect of drug treatment on reactive oxygen species generation in whole blood stimulated by OpZ at 48 hrs following myocardial I/R, as assessed by blood chemiluminescence (n = 4 sham-operated, and n = 6–12 I/R). (D) The effect of drug treatment on gene expression at 48 hrs following myocardial I/R, as assessed by qPCR of left ventricule (LV) homogenates (n = 7–8). (E) Representative photomicrographs of mid-ventricular LV sections of a mouse treated with vehicle or BIIL 284 and SR 27417; scale bar = 200 and 20 μm for left (100 × ) and right (400 × ) images respectively. (F) Representative photomicrographs and bar graphs showing the effect of BIIL 284 pre-treatment on infarct size in PAFR−/− mice (n = 4–5 mice per group). Data are mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus water; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 versus BIIL 284; ψψψP < 0.001 versus SR 27417; †P < 0.05 versus sham-operated mice.