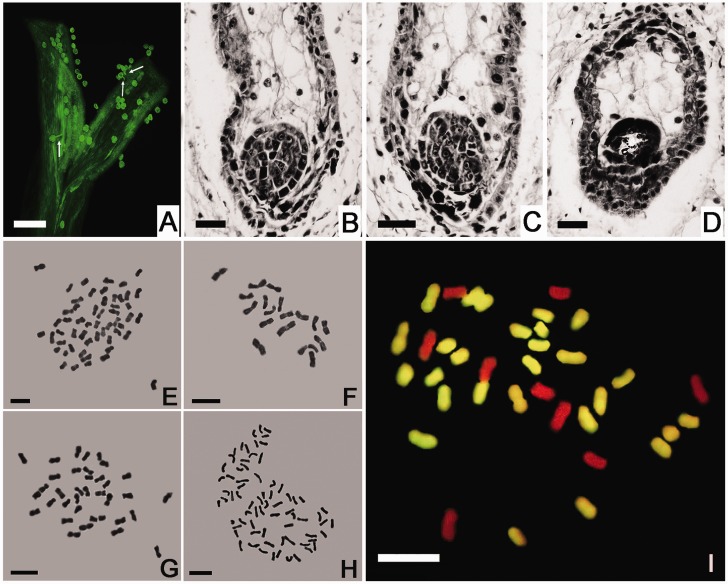
Fig. 2.—
The germination of L. paludosum pollen on the Chrysanthemum morifolium stigma and the development of the hybrid embryo. (A) Pollen germination 12 h postpollination. Bar: 100 μm. (B, C) Two globular stage proembryos with a degenerating endosperm in a 12-DAP ovule. (D) A degenerated globular proembryo in an 18-DAP ovule. Bar: 20 μm. (E–H) The mitotic chromosomes of (E) C. morifolium cv. “Zhongshanzigui” (2n = 54), (F) Leucanthemum paludosum (2n = 18), (G) the C. morifolium × L. paludosum amphihaploid (2n = 36), and (H) the C. morifolium × L. paludosum amphidiploid (2n = 72). Bar: 5 μm. (I) GISH analysis of the C. morifolium × L. paludosum amphihaploid. The chromosomes were probed with labeled C. zawadskii genomic DNA; the 27 yellow fluorescing chromosomes were inherited from C. morifolium, and the nine unlabeled (red) ones from L. paludosum. Bar: 5 μm.