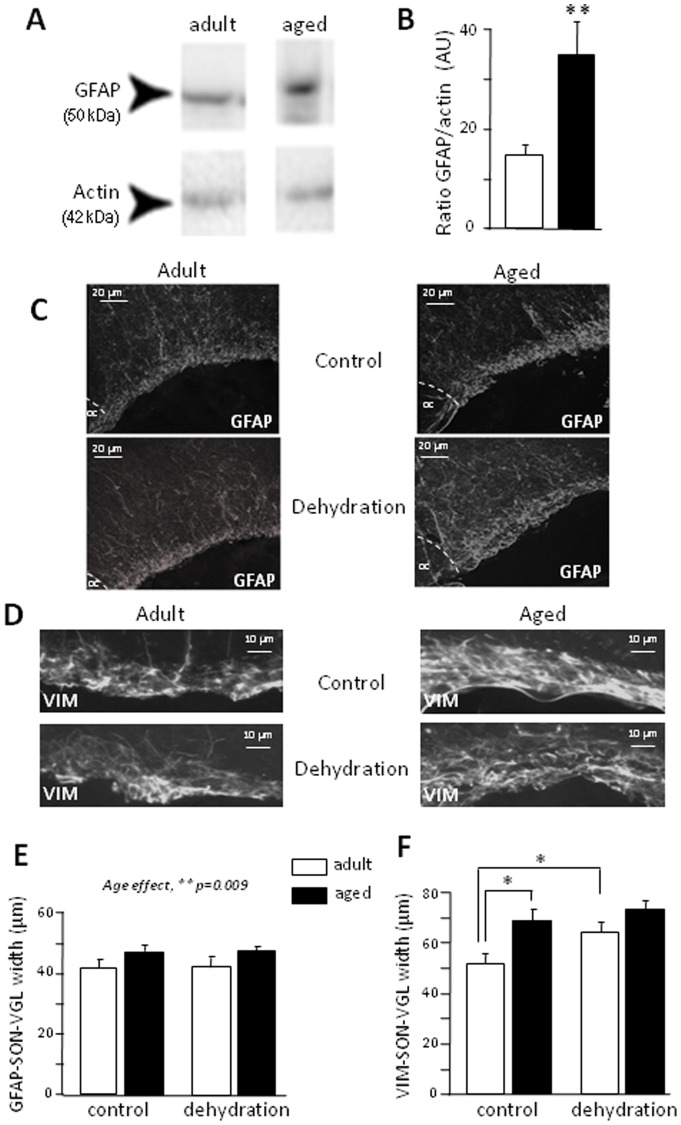
Figure 3. Morphofunctional characteristics of GFAP- and vimentin-positive cells during aging and dehydration: consequences for dual AVP/apelin neuron function.
A- Western blot of GFAP in adult and aged rats. B-Levels of GFAP mRNA in the SON of adult and aged rats (GFAP/actin, expressed in AU). C- Immunohistochemistry of GFAP-IR cells in the SON of adult and aged rats subjected to dehydration (dehy). The dotted line indicates the limit of the optic chiasma. OC: optic chiasma. D- Immunohistochemistry of vimentin (VIM)-IR cells in the SON-VGL of adult and aged rats under control conditions and following dehydration. E- SON-VGL width, after staining for GFAP, in adult and aged rats under control conditions and following dehydration. F- SON-VGL width, after staining with vimentin (VIM), in adult and aged rats under control conditions or following dehydration. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01.