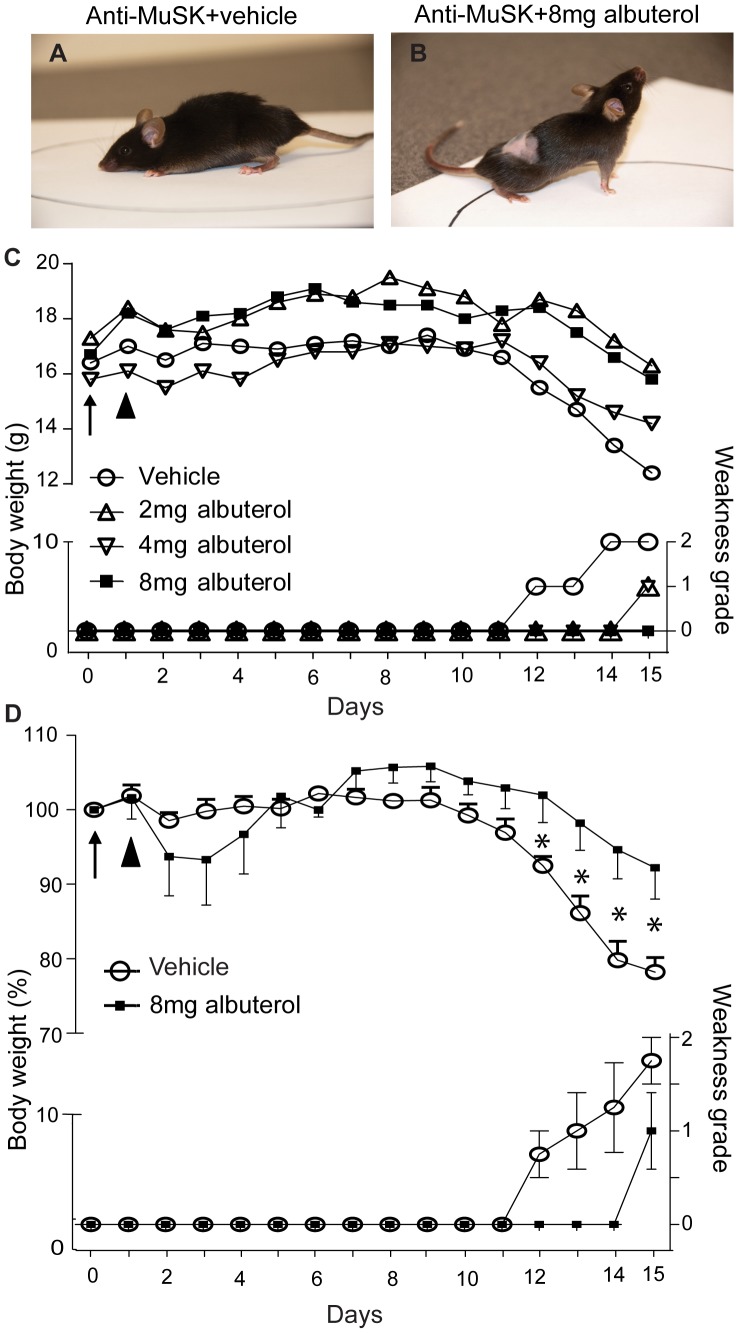
Figure 1. Effects of anti-MuSK IgG and albuterol on muscle weakness and body weight.
Mice received 15 daily intraperitoneal injections of anti-MuSK-positive patient IgG. Albuterol was delivered continuously via a subcutaneous minipump. (A) Example of typical whole-body weakness in a mouse on day 15 of the anti-MuSK IgG injection series (chin down, flaccid tail, and limb weakness). This mouse was treated with vehicle only. (B) A physically active mouse on day 15 of the anti-MuSK IgG injection series with albuterol treatment (8 mg/kg/day). (C) Pilot dosage trial. Body-weight and weakness grading traces are shown for single mice that received daily injections of anti-MuSK IgG and were treated with 2, 4 or 8 mg/kg/day albuterol, or vehicle. Body weights are shown on the left ordinate while weakness grades are indicated on the lower right ordinate. A minipump delivering either albuterol or vehicle was implanted subcutaneously on day 0 (arrow). The arrowhead indicates a single cyclophosphamide injection to suppress an active immune response to the human IgG. (D) Normalized body weights and weakness grades for mice receiving daily injections of anti-MuSK IgG and treatment with 8 mg/kg/day albuterol (filled squares) or vehicle (open circles). Error bars in panel D represent the mean ± SEM for n = 4 mice in each treatment group (*P<0.05, unpaired Student’s t test).