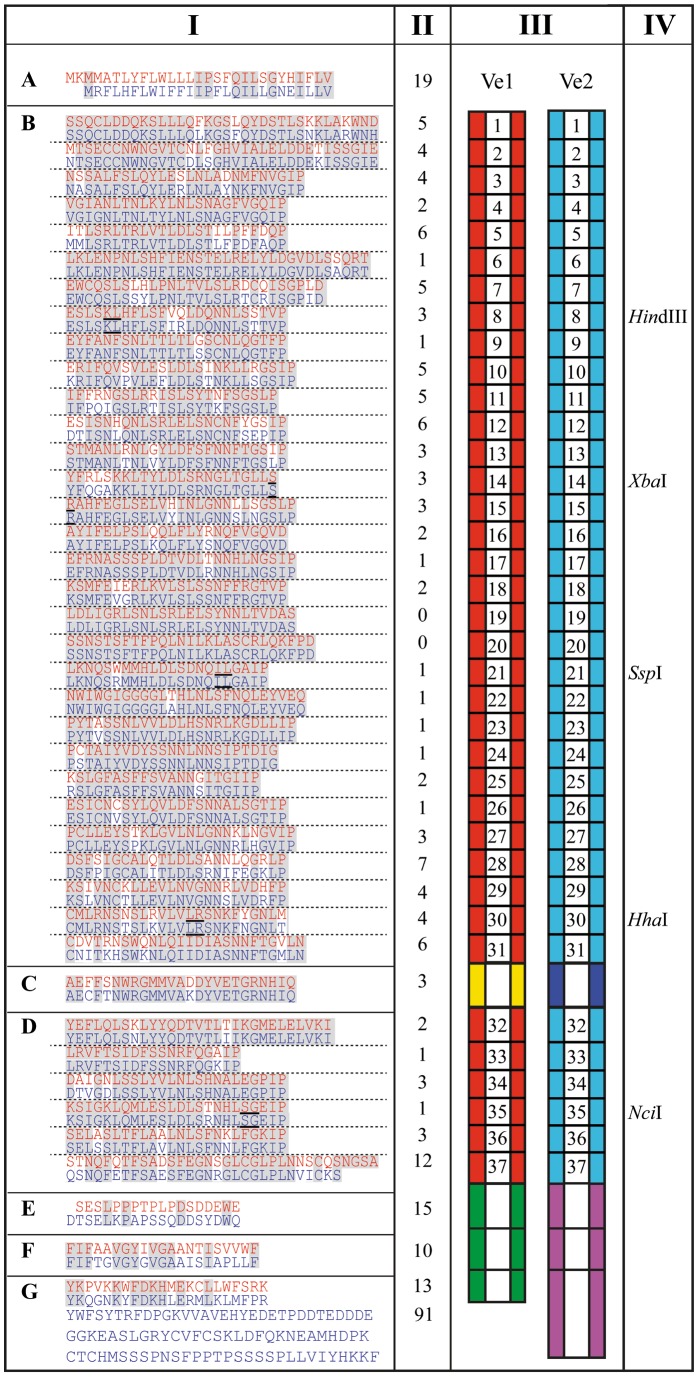
Figure 2. Protein sequence alignment of Ve1 and Ve2.
Columns from Left to Right, I: Alignment of Ve1 (red) and Ve2 (blue) divided into: N-terminal signal peptide (A), leucine-rich repeat (eLRR) domains with each of the 37 eLRRs separated by a dashed line (B and D), non-LRR island domain (C), extracytoplasmic domain (E), transmembrane domain (F), and cytoplasmic domain (G). Conserved amino acid residues between Ve1 and Ve2 are highlighted. The underlined amino acid residues in eLRR8, eLRR14-15, eLRR21, eLRR30, and eLRR35 indicate positions that were used for domain swaps. II: Number of different amino acids between Ve1 and Ve2. III: Schematic representations of Ve1 and Ve2. Red and turquoise boxes represent the 37 eLRR domains of Ve1 and Ve2, respectively. Yellow and dark blue boxes represent the non-LRR island domains of Ve1 and Ve2, respectively. Green and mauve boxes represent the extracytoplasmic, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic domains of Ve1 and Ve2, respectively. IV: Restriction enzyme recognition site in eLRR8, eLRR14-15, eLRR21, eLRR30, and eLRR35 that were used for domain swaps.