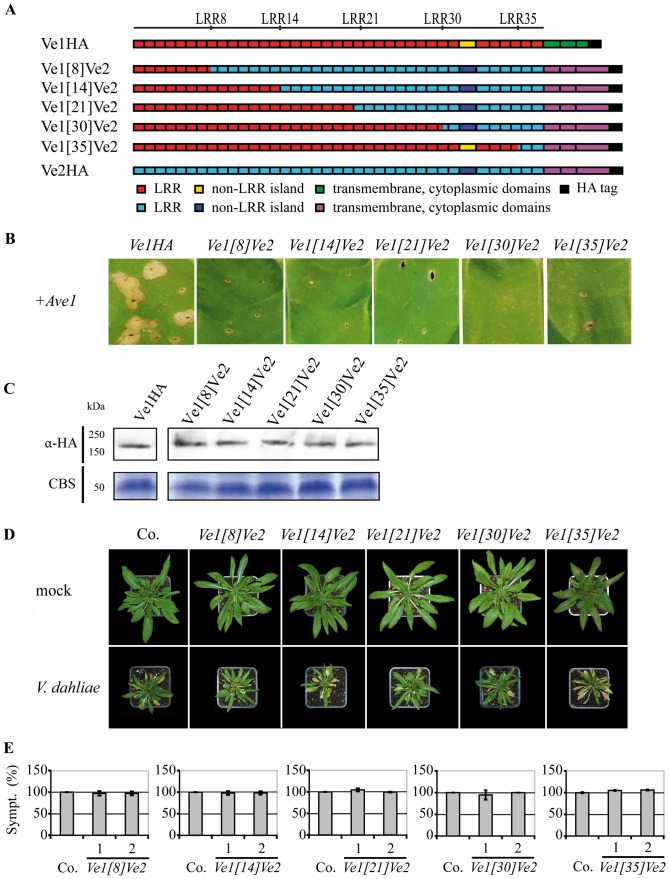
Figure 3. Functional characterization of Ve chimeric proteins that contain the C-terminus of Ve2.
(A) Schematic representations of transgenically expressed Ve1 (Ve1HA) and Ve2 (Ve2HA) and the proteins encoded by the chimeric genes Ve1 [8] Ve2, Ve1 [14] Ve2, Ve1 [21] Ve2, Ve1 [30] Ve2, and Ve1 [35] Ve2. The numbers indicate the eLRR at the site of the swap. (B) Chimeras containing the Ve2 C-terminus do not induce HR upon coinfiltration with Ave1. (C) Stability of chimeric Ve proteins is shown by immunoblotting using HA antibody (α-HA). Coomassie-stained blots (CBS) showing the 50 kDa Rubisco band present in the input samples confirm equal loading. (D) Typical appearance of non-transgenic sgs2 (Co.) and transgenic Arabidopsis sgs2 lines upon mock-inoculation or inoculation with V. dahliae race 1. Photographs were taken at three weeks post inoculation and show a representative plant of the non-transgenic sgs2 as well as a representative plant from one of the independent transgenic lines. (E) Quantification of Verticillium wilt symptoms (Sympt.) in Co. and transgenic lines. Bars represent quantification of symptoms presented as percentage of diseased rosette leaves with standard deviation. Co. is set to 100%. No significant differences were monitored when compared with Co. (P<0.001). For each construct two independent transgenic lines are shown (1, 2).