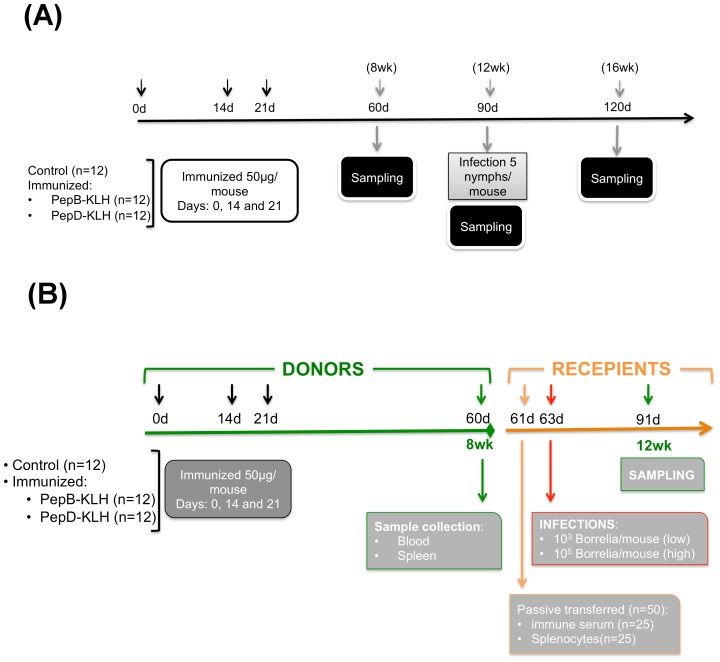
Figure 4. Summary of the study design.
(A) Schematic representation of the efficacy study. C3H/HeN mice were immunized with peptide B or D derived from the VWFA domain of BB0172 conjugated to KLH and administered at 50 µg/mouse with equal volume of TiterMax® Gold (Sigma-Aldrich) at days 0, 14 and 21. Eight weeks post-priming, a subgroup of mice (4/treatment) were sampled to determine antibody levels and pathological side effects. Twelve weeks post-priming a second subgroup of mice (4/treatment) were euthanized and sampled for antibody levels in blood, T-cell activity (from draining lymph nodes and spleens) and tissue damage. At the same time, a final group of 4 mice/treatment was infected by tick challenge, utilizing 8 infected Ixodes scapulars nymphs/mouse (containing around 150 Borrelia/nymph). Sixteen weeks post-priming mice were euthanized and protection evaluated by determining bacterial recovery from tissues as well as bacterial burden, tissue damage and antibody levels in blood. (B) Schematic representation of the passive transfer experiment conducted during phase II. Donor C3H/HeN were immunized with peptide B or D administered at days 0, 14, and 21. Eight weeks post-priming, donor mice were euthanized and blood and spleens were collected. Serum and splenocytes were isolated and passively transferred to recipient mice. Two-days after transfer mice were infected with either a low (103 spriochetes/mouse) or a high (105 spirochetes/mouse) dose of B. burgdorferi B31 by subcutaneous inoculation. Four weeks post-challenge mice were euthanized and protection was evaluated.