FIGURE 4.
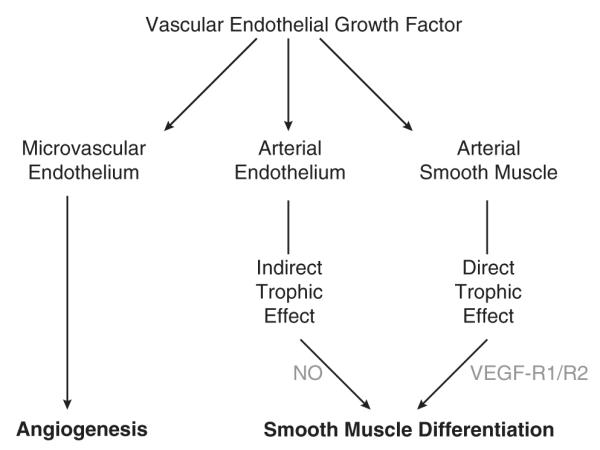
VEGF exerts trophic effects on vascular smooth muscle. The traditional view of VEGF held that this growth factor acted largely on the microvascular endothelium to promote angiogenesis.19 More recent evidence, however, has demonstrated a broad variety of effects of VEGF on many different cell types.23 Most importantly, it is now clear that VEGF can act indirectly through the vascular endothelium and directly through VEGF receptors on smooth muscle cells, to influence smooth muscle differentiation. NO indicates nitric oxide; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.27,28
