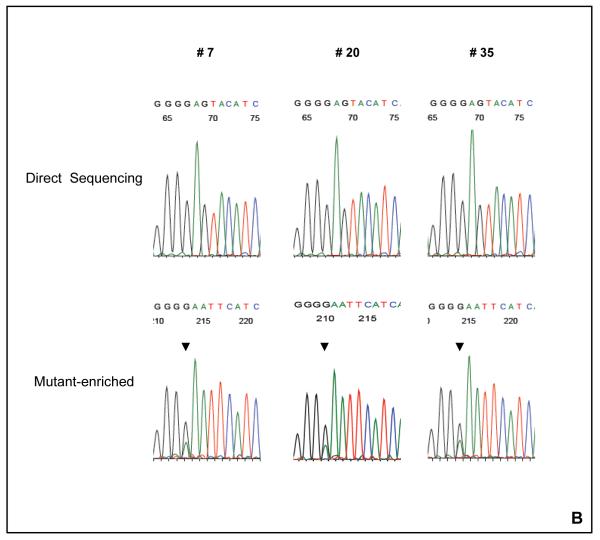
Figure 1. The detection of AKT1 E17K mutation with the mutant-enriched sequencing method.
(A) The schematic for the mutant-enriched sequencing method for AKT1 E17K. Briefly, a unique restriction enzyme site EcoRI was introduced by mismatch PCR to the wild-type DNA strand but not the mutant sequence in the first round of PCR. The mismatch primer (AKT1ME-R) has two nucleotide substitutions (G → A and A→ T). Subsequent EcoRI digestion of the wild-type DNA strands would allow preferential amplification of the mutant templates in the second round of PCR. (B) Detection of AKT1 E17K mutation by mutant-enriched method. AKT1 E17K mutation was not detectable by the conventional direct sequencing method in cases # 7, # 20 and # 35, but was enriched and visible with the mutant-enriched sequencing method.