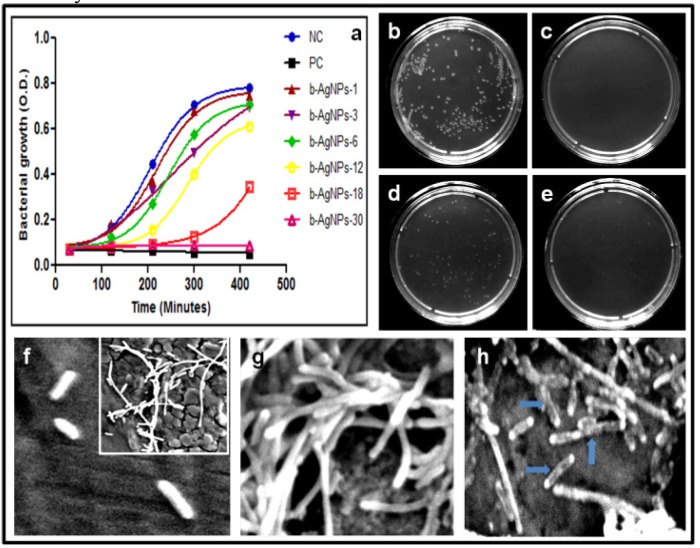
Figure 2.
Study of anti-bacterial activities: (a) liquid growth inhibition kinetics of E. coli using different concentrations of b-AgNPs. b-AgNP-30 (at 30 µM) shows almost 100% growth inhibition. Ampicillin has been used as a positive control (PC) & NC: negative control or untreated E. coli. The numerical number indicates the concentration of b-AgNPs in µM, (b-e) optical images of bacterial colonies formed by E. coli cells i.e. colony counting assay (after 24 h): b: Control, c:Ampicillin (100μg/ml), d: b-AgNPs (18 μM), e: b-AgNPs (30μM) and (f-h) SEM images of E. coli cells (f) without being treated (control), (g) treated with Olax for 1 hour, (h) treated with b-AgNPs (30 µM) for 1 hour. The SEM images show the silver nanoparticles damages the bacterial cell membrane (marked by blue arrow), whereas, the bacterial membranes of untreated and treated E. coli with Olax is intact.