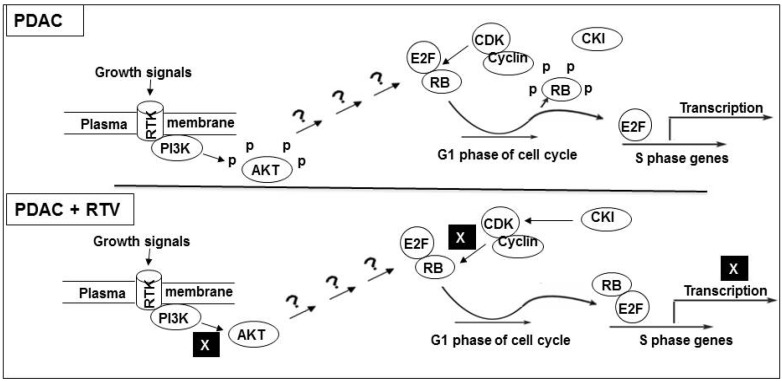
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of signaling pathways from cell surface to nucleus modulated by ritonavir in PDAC: Upper panel: In the absence of ritonavir (RTV), growth signals from receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) are conveyed to AKT via phosphotidyl inositol 3 kinase (PI3K). RB is inactivated by phosphorylation of cyclin-CDK complexes, resulting in the activation of E2F-1 transcription. E2F-1 target genes encode proteins involved in expression of S phase genes; Lower panel: In the presence of ritonavir, growth signals are inhibited by de-phosphorylation (activation) of RB, resulting in complex formation with E2F-1. This process inhibits transcription of S phase genes in two ways, passively via sequestration of E2F-1 and actively via the RB-E2F-1 complex.