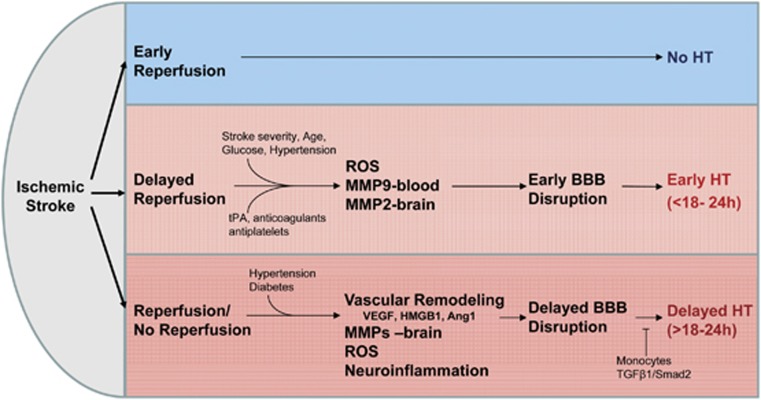
Figure 3.
Early reperfusion reduces the risk of hemorrhagic transformation (HT). Delayed reperfusion increases the BBB disruption and the risk of HT. ROS, leukocyte-derived MMP-9, and brain-derived MMP-2 have an important role in producing early BBB disruption and early HT. In contrast, brain-derived vascular remodeling, MMPs (MMP-9, MMP-2, and MMP-3), other brain proteases (plasmin, endogenous tPA, urokinase (uPA), and cathepsins), ROS, and neuroinflammation contribute to delayed BBB and delayed HT. A subset of monocytes that enter brain may prevent delayed HT. BBB, blood–brain barrier; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SMAD, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog; TGFβ1, transforming growth factor β1; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; HMGB1, high-mobility-group-box-1.