Figure 1.
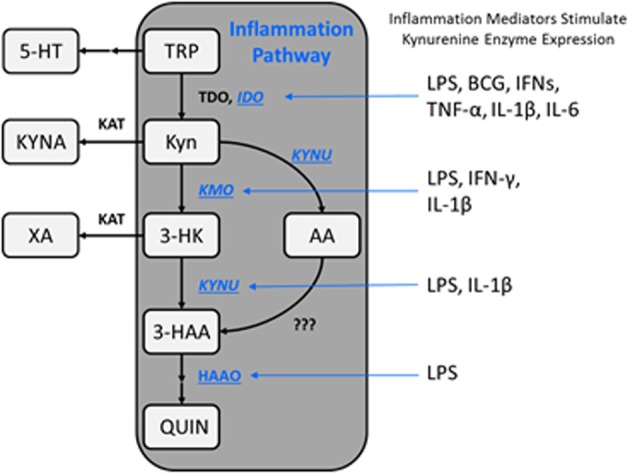
Schematic representation of the kynurenine metabolic pathway. The kynurenine pathway is commonly segregated into two distinct branches that are regulated by KATs and KMO, as well as the availability of l-kynurenine within the brain. Additionally, kynurenine metabolism is regulated by a variety of proinflammatory mediators which impact enzyme expression levels, thereby altering substrate availability and metabolite formation favoring the KMO branch of the pathway under immune-related pathological conditions. TRP, tryptophan; 5-HT, serotonin; Kyn, kynurenine; KYNA, kynurenine acid; 3-HK, 3-hydroxykynurenine; AA, anthranilic acid; XA, xanthurenic acid; 3-HAA, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid; QUIN, quinolinic acid; IDO, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase; KAT, kynurenine aminotransferase; KMO, kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; KYNU, kynureninase; HAAO, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid oxidase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; BCG, bacillus Calmette-Guerin; IFNs, interferons; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin.
