Fig. 2.
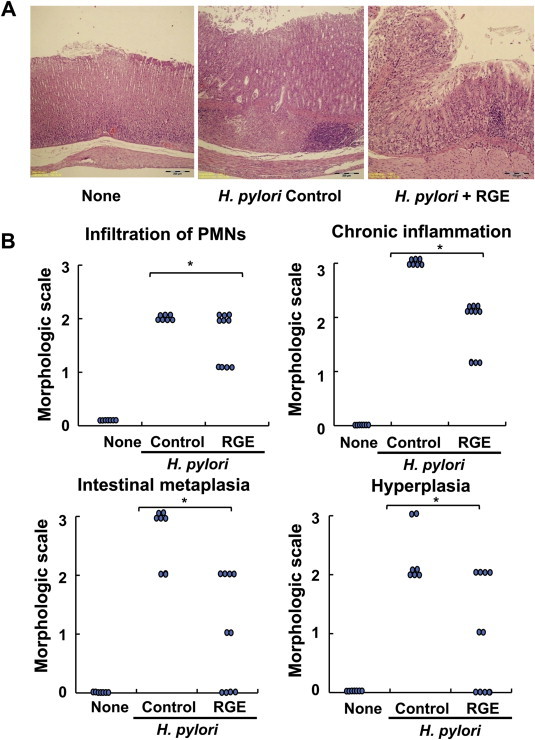
Effect of Korean Red Ginseng extract (RGE) on Helicobacter pylori-induced histological changes in gastric mucosal regions of Mongolian gerbils. (A) Gastric mucosal sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Microscopic images were obtained at magnification of ×200. (B) The inflammatory responses of gastric mucosa were graded according to morphologic criteria: Grade 0, normal; Grade 1, mild; Grade 2, moderate; and Grade 3, severe. The following characteristics of gastric lesions were recorded: polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) infiltration, chronic inflammation such as mononuclear cells infiltration and lymphoid nodules formation, intestinal metaplasia, and hyperplasia and formation of heterotopic proliferative glands. None, animals without H. pylori infection that were fed the control diet; H. pylori control, animals with H. pylori infection that were fed the control diet; and H. pylori + RGE, animals with H. pylori infection that were fed a diet supplemented with RGE. *Statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) between H. pylori control and H. pylori + RGE.
