FIGURE 1.
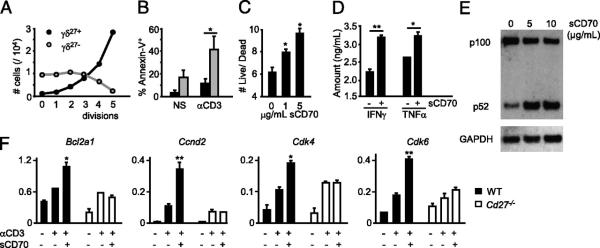
CD27 costimulation provides antiapoptotic and proliferative signals to γδ T cells. Peripheral γδ27+ (black filling) and γδ27− (gray filling) cells (A, B) or total γδ cells (C, D) were FACS-sorted from pooled spleen and LNs of C57BL/6 mice, stained with CFSE, cultured with allophycocyanin without (nonstimulated [NS]) or with anti-CD3ε mAb (αCD3) for 72 h, and then stained with Annexin V. A, Absolute numbers per cell division calculated based on CFSE dilution kinetics. B, Percentages of Annexin V+ (apoptotic) cells. C, Ratio of Annexin V− (live)/Annexin V+ (dead) cells among divided (CFSElo) cells when sCD70 was added to the cultures. D, Cytokine bead array analysis for IFN-γ and TNF-α in the cultures’ supernatants, with or without sCD70. E, FACS-sorted γδ27+ cells were cultured for 16 h with anti-CD3 (1 μg/ml) and 5–10 μg/ml sCD70 or 10 μg/ml human IgG1 control. Immunoblotting analyses were performed on total cellular extracts with indicated Abs. F, γδ cells, FACS-sorted from Cd27+/+ or Cd27−/− mice, were cultured for 6 h with or without anti-CD3 (1 μg/ml, plate-bound) and sCD70 (5 μg/ml). Quantitative real-time PCR data for Bcl2a1, Cyclin D2, CDK4, and CDK6 in arbitrary units normalized to the housekeeping gene Efa1. Significant increases relative to anti-CD3 samples are indicated. Data in A–F are representative of three independent experiments (each involving four to six animals) with consistent results. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
