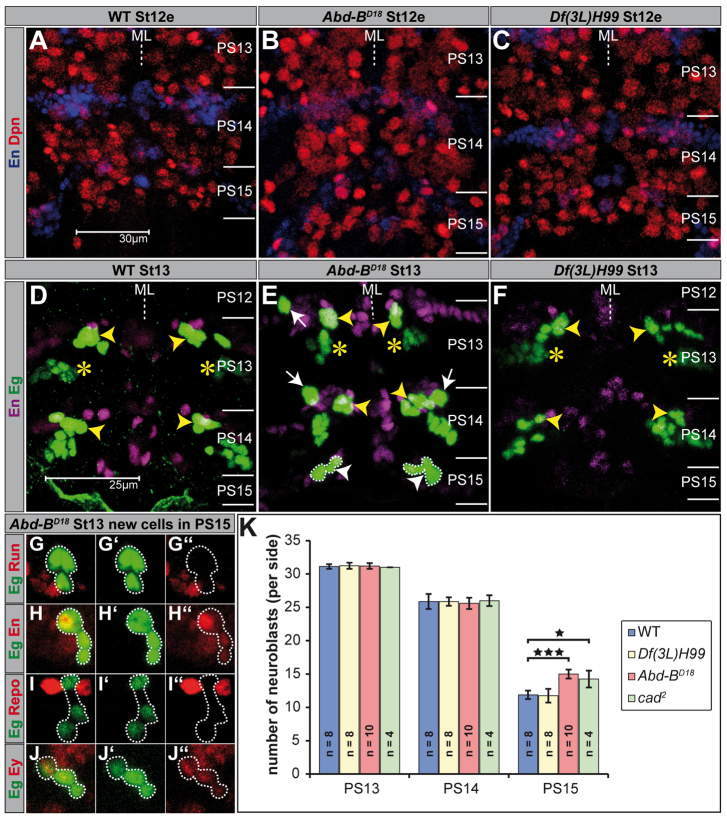
Fig. 1.
Abdominal-B suppresses the formation of neuroblasts in parasegment 15. (A-F) Flat preparations (maximum projections) of St12e and St13 embryos of the indicated genotype double-stained as illustrated. PSs are depicted on the right and their borders are illustrated by a solid line. (A-C) Dpn serves as a universal NB marker. (D-F) NB2-4 (dorsal location) and NB3-3 clones (ventral location) are En negative and indistinguishable in maximum projections of PS13 (yellow asterisks). The typical medial location of the NB7-3 cluster (En positive) is marked by yellow arrowheads. (D,F) The abdominal NB6-4 clones (consisting of two glia) already downregulated Eg expression. (E) Transformation of abdominal NB6-4 into thoracic fate is indicated by appearance of the neuronal subclone, showing constant Eg expression (white arrows). Ectopic NB7-3 cells in PS15, which are not found in wild type or in Df(3L)H99 mutant embryos, are surrounded by broken lines and indicated by white arrowheads. (G-J′) The ectopic NB7-3 cells in PS15 of Abd-BD18 mutant embryos were identified by double-staining against Eg (green) and various molecular markers as indicated (red). (K) Statistics for the total number of Dpn-positive NBs (per side) of the indicated genotypes in PS13, PS14 and PS15, respectively. *P<0.05; ***P<0.001. Error bars represent s.d. ML, midline; WT, wild type.