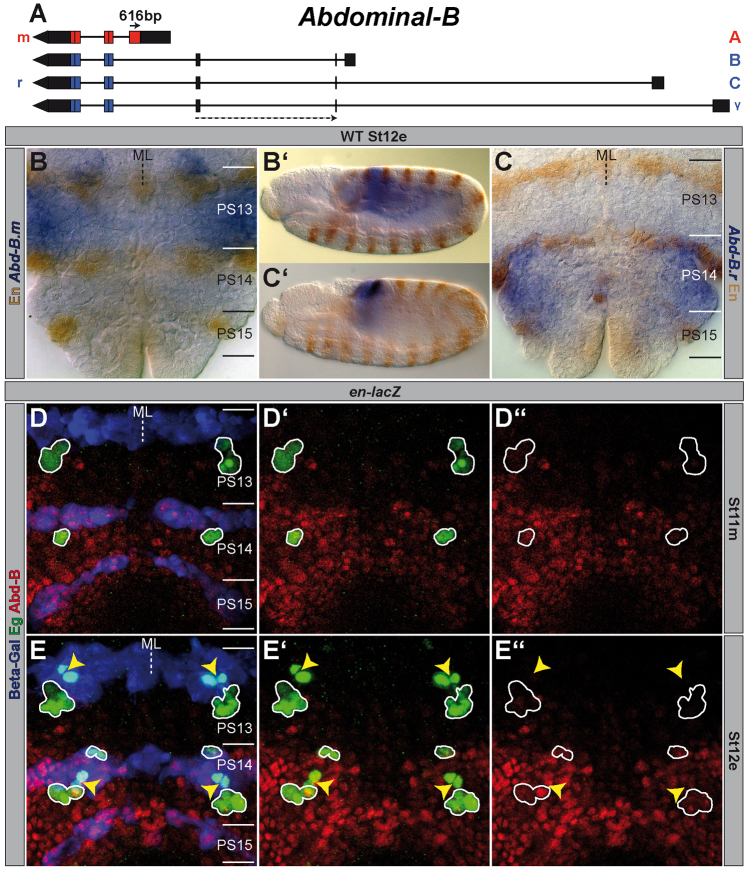
Fig. 3.
Expression of different Abdominal-B elements in wild type. (A) The Abd-B gene (drawn to scale) according to FlyBase (McQuilton et al., 2012). Lines depict intron sequences; boxes mark exons (black ones show UTRs, coloured ones CDSs). The localisation of the exon probes are illustrated by arrows (solid one=Abd-B.m (616 bp); stippled one=Abd-B.r (220 bp) spanning over two exons). (B,C) In situ hybridisation of Abd-B.m (B) or Abd-B.r (C) in a wild-type St12e VNC (flat preparation). PSs are depicted on the right and their borders are illustrated by a solid line. (B′,C′) Same stainings in whole mount. (D,E) Flat preparations (maximum projections) of St11m and St12e en-lacZ embryos triple-stained against Abd-B (both isoforms), Eg and beta-galactosidase (Beta-Gal). (E) NB7-3 of PS13 and PS14, which underwent their first division, are marked by yellow arrowheads. All other wild-type Eg-positive cells are encircled. Please note the intensive expression of Abd-B.r in the En stripe of PS15, where the formation of NB7-3 is inhibited. (D′,E′) Abd-B and Eg staining. (D′,E′) Abd-B expression. ML, midline; WT, wild type.