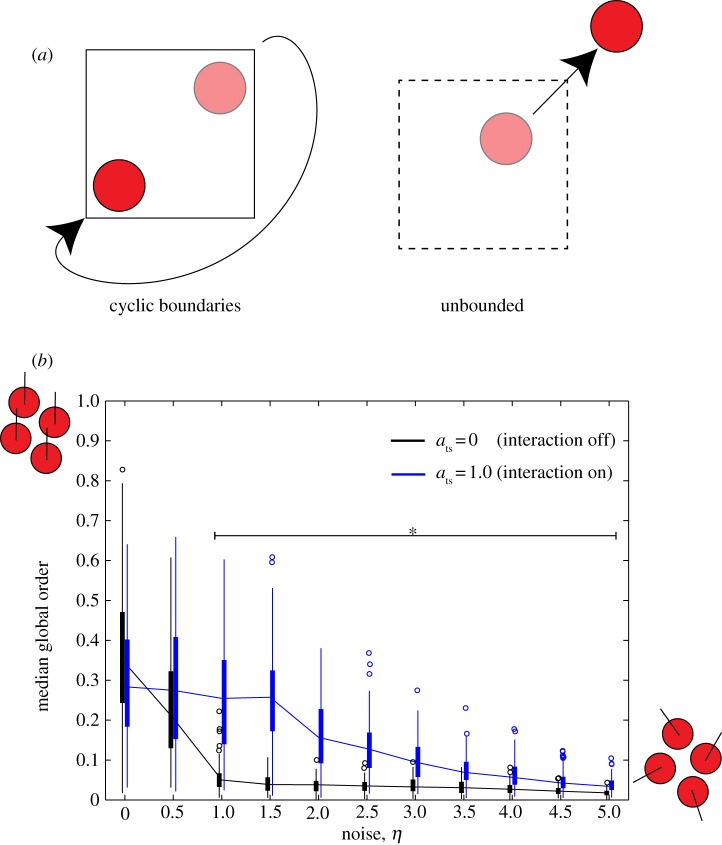
Figure 3.
(a) Comparison of a system with cyclic boundary conditions with an unbounded system. Squares indicate areas of inoculation. In a system with cyclic boundary conditions, cells leaving the area of inoculation will re-enter the area at the diametrically opposite point, maintaining its polarization. In an unbounded system, the cell is not spatially constrained and may leave the area of inoculation. (b) Global order parameter as a function of noise in an unbounded system. The order of the system decreases rapidly as η increases. When ats = 1.0, the order increases for all positive values of η compared with simulations in which ats = 0. Asterisks indicate a significant difference between the ats = 1.0 and ats = 0 simulations (p < 0.001).