Figure 3.
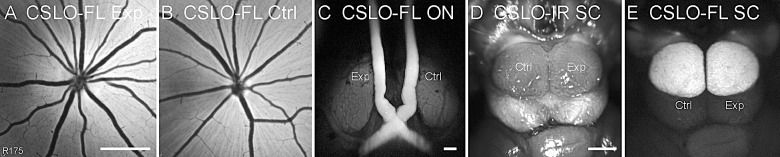
Results of the anterograde axonal transport assay 1 week after acute IOP elevation to 50 mm Hg for 8 hours in the experimental eye in one representative animal. (A, B) The CSLO-FL images of the ocular fundi obtained in vivo from the experimental (Exp [A]) and control (Ctrl [B]) eyes 24 hours after bilateral intravitreal injections of CTB demonstrate successful CTB uptake and transport by RGCs along their axons to the optic disc. (C) Postmortem CSLO-FL of the optic nerves and chiasm shows equivalent fluorescence along both nerves, indicating intact anterograde axonal transport along experimental and control pathways of the optic nerve. (D) Postmortem CSLO infrared (IR) image of the dorsal midbrain shows the position of the superior colliculi for orientation. (E) Postmortem CSLO-FL image of the superior colliculi shows equivalent intensity and coverage of CTB fluorescence between colliculi, indicating that anterograde axonal transport to the colliculi is intact along both experimental and control pathways. Quantitative results are summarized in Table 2. Scale bars: 1 mm (A applies to A and B; D applies to D and E).
