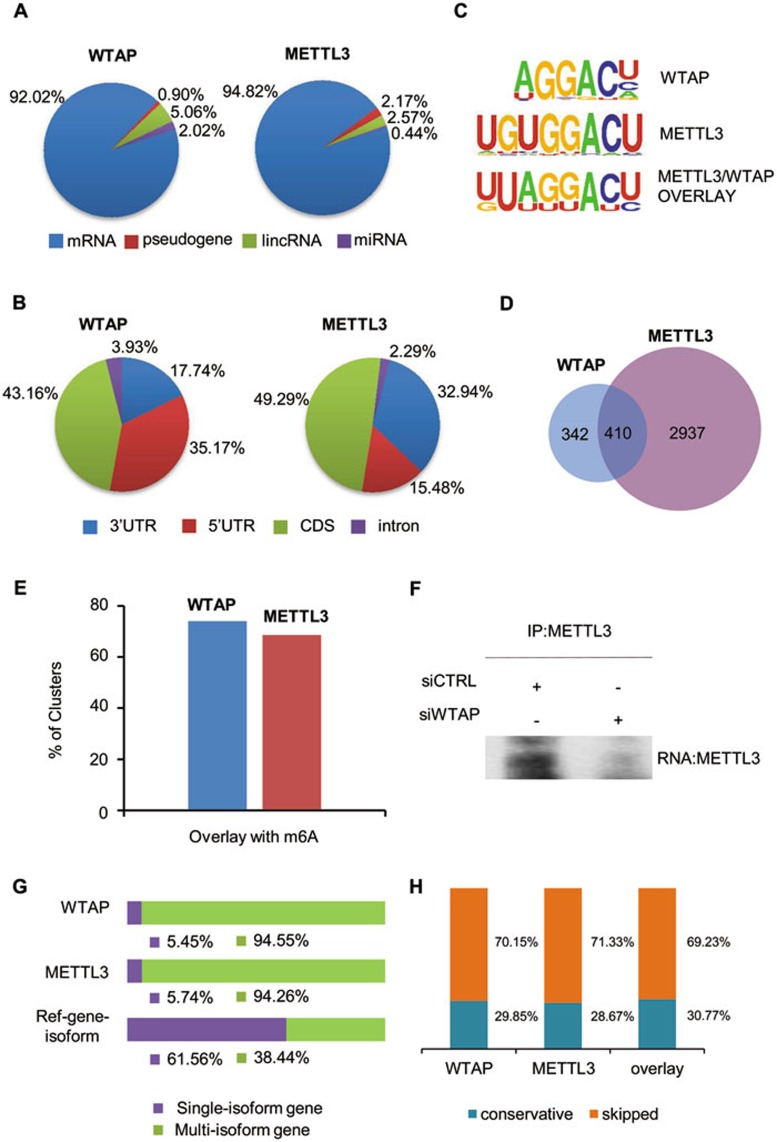
Figure 3.
METTL3 and WTAP bind m6A consensus sequence in mRNA and affect gene expression and alternative splicing. (A) Percentage of various RNA species bound by WTAP and METTL3 based on PAR-CLIP analyses. The WTAP- and METTL3-binding clusters were identified by PARalyzer algorithm. Annotation of clusters was based on the human Ensembl gtf file (version 72, hg19). The majority of binding sites of WTAP and METTL3 were located in mRNA. (B) Pie chart depicting the distribution of binding clusters in mRNA based on PAR-CLIP sequence clusters for WTAP and METTL3 after normalization of the overall length of the different transcript regions. Length of these different transcript regions was extracted from Ensembl annotations and the distribution percentage of clusters in these regions were normalized by their length. (C) Enriched sequence motif analysis of binding clusters indentified by PAR-CLIP. Upper panel, WTAP-binding motif (P = 1e-14); middle panel, METTL3-binding motif (P = 1e-13); lower panel, binding motif obtained when only genes found in both WTAP- and METTL3-binding clusters were included (P = 1e-19). Binding motifs were computed by the HOMER program. (D) Venn diagram of the overlapping genes with binding clusters of WTAP and METTL3 in the PAR-CLIP samples. (E) Percentage of WTAP/METTL3 clusters in CDS and UTR regions overlapped with m6A sites. (F) HeLa cells were transfected with siCTRL or siWTAP and Myc-METTL3 for 48 h as indicated. The cell lysates were then subjected to PAR-CLIP using anti-Myc. The pulled down RNA products in the RNA-METTL3 complex were labeled by Biotin and detected by Biotin chemiluminescent nucleic acid kit. (G) Percentage of WTAP- (711 multi-isoform and 41 single-isoform) and METTLE3- (3 155 multi-isoform and 192 single-isoform) binding mRNAs derived from single-isoform or multi-isoform genes and the reference Ensembl genes of human (P = 2.2e-16, Fisher test). (H) Percentage of constitutively or alternatively spliced exons adjacent to intronic binding clusters of WTAP (left), METTL3 (middle), overlap of WTAP and METTL3 (right). Supportive data were included in Supplementary information, Figures S4 and S5.