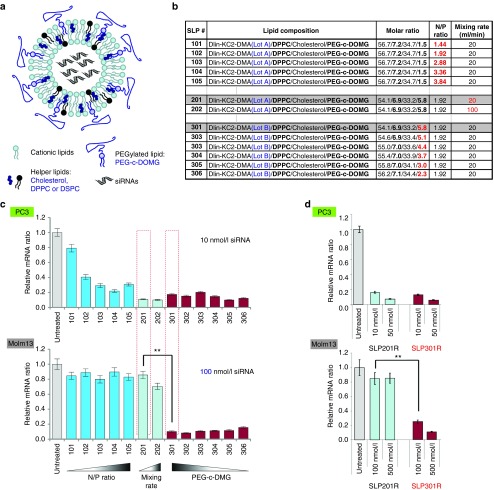
Figure 1.
Newly discovered SNALP-like lipid nanoparticles (SLPs) efficiently deliver siRNA into suspension leukemia cells. (a) Schematic representation of SLPs. (b) Composition of optimized SLPs with different N/P ratios (SLP100s), mechanical mixing rates (SLP200s), and percentages of PEG-c-DMG components (SLP300s). The differences among formulations were colored in blue or red. (c) Discovery of SLP300s able to efficiently knockdown KIF11 in suspension Molm13 leukemia cells. SLP100s-SLP300s were tested in easy-to-transfect adherent PC3 cells (upper panel) and hard-to-transfect suspension Molm13 cells (lower panel). KIF11 mRNA knockdown was measured by quantitative RT-PCR after 24 hours of siRNA transfection. Error bars represent mean ± SD. P value is calculated using a Student's t-test. SLP201 and SLP301, prepared from the same formula, are boxed in red. (d) Only SLP301R is able to efficiently knockdown KIF11 in Molm13 cells. SLP201R, repeat of SLP201 with Lot A of Dlin-KC2-DMA; SLP301R, repeat of SLP301 with Lot B of Dlin-KC2-DMA.