Figure 3.
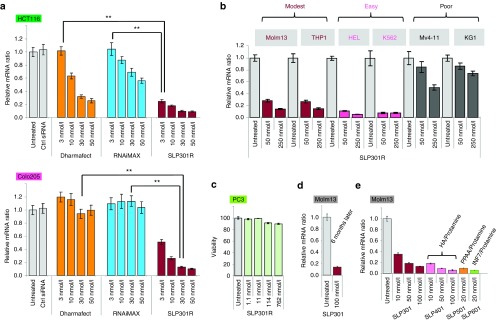
Alkylated DMA-containing SNALP-like lipid nanoparticles (SLPs) displayed superior in vitro siRNA transfection efficiency, low cellular toxicity and high stability in both adherent cells and suspension leukemia cells. (a) ClMDMA-containing SLP301R showed superior transfection efficiency compared with leading commercial siRNA transfection reagents. Control siRNA or increasing concentration of KIF11 siRNA were transfected using Dharmafect (Thermo Fisher), RNAiMAX (Invitrogen), or SLP301R into easily transfected HCT116 (upper panel) and poorly transfected Colo205 adherent cells (lower panel). KIF11 mRNA knockdown was measured by quantitative RT-PCR after 24 hours of siRNA transfection. Error bars represent mean ± SD. P value is calculated using a Student's t-test. (b) SLP301R is able to potently transfect multiple leukemia cell lines. Increasing concentration of KIF11 siRNA were transfected using SLP301R in six leukemia cell lines as indicated. (c) SLP301R encapsulating siRNA is not toxic for cells. Increasing concentration of luciferase siRNA as indicated was transfected into PC3 cells using SLP301R, and cell viability was measured by CellTiter-Glo at 24 hours after transfection. (d) SLP301R maintained Molm13 transfection efficiency after storage in 4 °C for 6 months. The efficiency of knockdown is measured by quantitative RT-PCR. (e) Incorporating biocompatible polymers into alkylated DMA-containing SLPs (Supplementary Table S1) as indicated leads to more than fivefold enhancement of Molm13 transfection efficiency. HA, hyaluronic acid; INF7, a glutamic acid-enriched cell penetrating peptide derived from influenza virus; PPAA, poly(propylacrylic acid).
