Figure 1. Citalopram administration does not attenuate infarct volume.
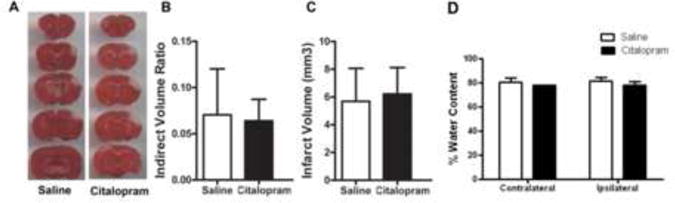
Citalopram was administered at 10 mg/kg (i.p.) 30 min after stroke and again at 24 and 48 hrs after stroke. A. Animals were sacrificed at 3 days after stroke. Infarct analysis was performed by staining brain sections with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC, red) for live mitochondria in brain cells. The white color area represents dead cells, those negative for TTC staining. B. Indirect volume analyses revealed no significant difference in infarct volume between the saline stroke control and citalopram treatment groups. (n=9 per group; Mean ± SD, p=0.61). C. Students T test revealed no significant differences in infarct volume (mm3) between the saline and citalopram treatment groups. (n=9 per group; Mean ± SD, p=0.73). Water content was measured using the dry-weight method. D. A two-way ANOVA test revealed no significant effect of treatment on cerebral edema after 72 hours. (n=6 per group; Mean ± SD, p=0.10).
